Ta-Nehisi Coates in The Atlantic:
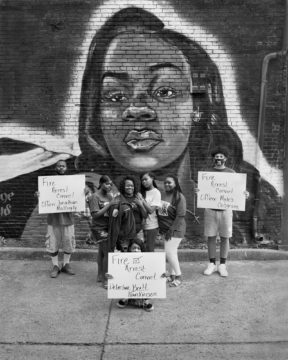 Kenny calls me in the middle of the night. He says, Somebody kicked in the door and shot Breonna. I am dead asleep. I don’t know what he’s talking about. I jump up. I get ready, and I rush over to her house. When I get there, the street’s just flooded with police—it’s a million of them. And there’s an officer at the end of the road, and I tell her who I am and that I need to get through there because something had happened to my daughter. She tells me I need to go to the hospital because there was two ambulances that came through, and the first took the officer and the second took whoever else was hurt. Of course I go down to the hospital, and I tell them why I am there. The lady looks up Breonna and doesn’t see her and says, Well, I don’t think she’s here yet. I wait for about almost two hours. The lady says, Well, ma’am, we don’t have any recollection of this person being on the way.
Kenny calls me in the middle of the night. He says, Somebody kicked in the door and shot Breonna. I am dead asleep. I don’t know what he’s talking about. I jump up. I get ready, and I rush over to her house. When I get there, the street’s just flooded with police—it’s a million of them. And there’s an officer at the end of the road, and I tell her who I am and that I need to get through there because something had happened to my daughter. She tells me I need to go to the hospital because there was two ambulances that came through, and the first took the officer and the second took whoever else was hurt. Of course I go down to the hospital, and I tell them why I am there. The lady looks up Breonna and doesn’t see her and says, Well, I don’t think she’s here yet. I wait for about almost two hours. The lady says, Well, ma’am, we don’t have any recollection of this person being on the way.
More here. (Note: At least one post throughout the month of February will be devoted to Black History Month. The theme for 2022 is Black Health and Wellness)

 We easily and often apply the label ‘postmodern’ to particular artworks, architecture, activities and ideas; it is harder to specify some common quality of postmodernism that they all share. Far more than other historical phases, ‘postmodernity’ seems almost to have been concocted by those who write about it. The term suggests an impossible realm – after the present yet somehow already present itself; the concept, judging by the copious literature on it, is precisely about imprecision and lack of essence, and better defined by what it is not. Jean-François Lyotard’s much-cited The Postmodern Condition (1979) diagnosed in it an absence of ‘grand narratives’ (Christianity, liberalism, Marxism), which have been abandoned due to lack of faith in the march of progress. We are left instead, in a Waste Land way, with fragments we have shored against our ruin. Now that modernism has exhausted outrage and authenticity, and been domesticated and canonised, all postmodern art and architecture can do is pastiche and appropriate earlier styles, blazoning their own lack of originality. A central principle of postmodernism is ‘intertextuality’, the notion that ‘any text is the absorption and transformation of any other’, in the words of Julia Kristeva.
We easily and often apply the label ‘postmodern’ to particular artworks, architecture, activities and ideas; it is harder to specify some common quality of postmodernism that they all share. Far more than other historical phases, ‘postmodernity’ seems almost to have been concocted by those who write about it. The term suggests an impossible realm – after the present yet somehow already present itself; the concept, judging by the copious literature on it, is precisely about imprecision and lack of essence, and better defined by what it is not. Jean-François Lyotard’s much-cited The Postmodern Condition (1979) diagnosed in it an absence of ‘grand narratives’ (Christianity, liberalism, Marxism), which have been abandoned due to lack of faith in the march of progress. We are left instead, in a Waste Land way, with fragments we have shored against our ruin. Now that modernism has exhausted outrage and authenticity, and been domesticated and canonised, all postmodern art and architecture can do is pastiche and appropriate earlier styles, blazoning their own lack of originality. A central principle of postmodernism is ‘intertextuality’, the notion that ‘any text is the absorption and transformation of any other’, in the words of Julia Kristeva.
 Chekhov is easier to know and read than the other Russian giants. He doesn’t look big or talk big. He’s funny on purpose. He shows us how to read him; he quietly attunes us to place and situation. We observe more than judge his characters’ actions; we detect their mental and emotional states through their physical symptoms. Chekhov began his professional career as a writer while in medical school. Even as he imagined the agitations and disruptions and occasional explosions of his characters, he was always also a doctor. He describes what it feels like to fall in love, to be pregnant and to miscarry, to bully one’s children, to flutter about helplessly while seeking someone to love, to have typhus, to cringe with embarrassment over a bespattering sneeze, to blather like a professor, to be struck dumb by love, to beg for sympathy, to grieve, to menace the innocent, to be conscious of but prey to one’s weaknesses, to be overworked to the point of hallucinating, to be ruthless.
Chekhov is easier to know and read than the other Russian giants. He doesn’t look big or talk big. He’s funny on purpose. He shows us how to read him; he quietly attunes us to place and situation. We observe more than judge his characters’ actions; we detect their mental and emotional states through their physical symptoms. Chekhov began his professional career as a writer while in medical school. Even as he imagined the agitations and disruptions and occasional explosions of his characters, he was always also a doctor. He describes what it feels like to fall in love, to be pregnant and to miscarry, to bully one’s children, to flutter about helplessly while seeking someone to love, to have typhus, to cringe with embarrassment over a bespattering sneeze, to blather like a professor, to be struck dumb by love, to beg for sympathy, to grieve, to menace the innocent, to be conscious of but prey to one’s weaknesses, to be overworked to the point of hallucinating, to be ruthless.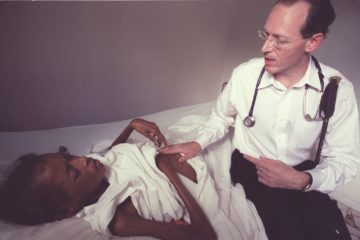 Paul Farmer, a physician, anthropologist and humanitarian who gained global acclaim for his work delivering high-quality health care to some of the world’s poorest people, died on Monday on the grounds of a hospital and university he had helped establish in Butaro, Rwanda. He was 62.
Paul Farmer, a physician, anthropologist and humanitarian who gained global acclaim for his work delivering high-quality health care to some of the world’s poorest people, died on Monday on the grounds of a hospital and university he had helped establish in Butaro, Rwanda. He was 62. Black humanity is unexceptional, Walter Johnson exhorts. Once we have taken up the debate of humanization versus dehumanization under slavery, we have already ceded critical ground. Like Johnson, midcentury Black Power activists understood that it was necessary to redirect such questions toward the matter of how the legacy of racial slavery continues to shape citizenship, democratic participation, and human rights, not just for black Americans but for people of color around the globe. Johnson’s essay offers profitable avenues for reappraising how Black Power is the conceptual bridge between Reconstruction-era black struggles for self-determination and Black Lives Matter’s present-day fight to end martial and economic violence against people of color.
Black humanity is unexceptional, Walter Johnson exhorts. Once we have taken up the debate of humanization versus dehumanization under slavery, we have already ceded critical ground. Like Johnson, midcentury Black Power activists understood that it was necessary to redirect such questions toward the matter of how the legacy of racial slavery continues to shape citizenship, democratic participation, and human rights, not just for black Americans but for people of color around the globe. Johnson’s essay offers profitable avenues for reappraising how Black Power is the conceptual bridge between Reconstruction-era black struggles for self-determination and Black Lives Matter’s present-day fight to end martial and economic violence against people of color. In 1975, Finnissy witnessed Soviet pianist Sviatoslav Richter
In 1975, Finnissy witnessed Soviet pianist Sviatoslav Richter 
 The biggest argument I’ve ever witnessed was about whether men had landed on the moon. Some years ago, at dinner—paella and wine—a chemist with a Ph.D. from Stanford suggested that the moon landing had been a hoax. This did not go over well with his father-in-law at the head of the table. At first I didn’t understand what I was hearing—I didn’t know then how many people believe the moon landing to be a fiction. Soon the men were roaring, the chemist’s brother-in-law got involved: “Of all the boneheaded bullshit to come pouring out of your face …” “Well, how do you explain …” Threats were flung, neck veins swelling, a hand slammed on the table, a knife clattered to the floor. We joked about it recently, the brother-in-law and I, recalling the scene, eating pasta with clams and garlic, and he asked me, “You’ve read the Apollo 11 eulogy speech, right?” I hadn’t. “Read it,” he said.
The biggest argument I’ve ever witnessed was about whether men had landed on the moon. Some years ago, at dinner—paella and wine—a chemist with a Ph.D. from Stanford suggested that the moon landing had been a hoax. This did not go over well with his father-in-law at the head of the table. At first I didn’t understand what I was hearing—I didn’t know then how many people believe the moon landing to be a fiction. Soon the men were roaring, the chemist’s brother-in-law got involved: “Of all the boneheaded bullshit to come pouring out of your face …” “Well, how do you explain …” Threats were flung, neck veins swelling, a hand slammed on the table, a knife clattered to the floor. We joked about it recently, the brother-in-law and I, recalling the scene, eating pasta with clams and garlic, and he asked me, “You’ve read the Apollo 11 eulogy speech, right?” I hadn’t. “Read it,” he said.
 JARVIS GIVENS
JARVIS GIVENS On Aug. 6, 1845, Frederick Douglass set sail on a speaking tour of England and Ireland to promote the cause of antislavery. He had just published “The Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass,” an instant best seller that, along with his powerful oratory, had made him a celebrity in the growing abolition movement. No sooner had he arrived in Britain, however, than Douglass began to realize that white abolitionists in Boston had been working to undermine him: Before he’d even left American shores, they had privately written his British hosts and impugned his motives and character.
On Aug. 6, 1845, Frederick Douglass set sail on a speaking tour of England and Ireland to promote the cause of antislavery. He had just published “The Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass,” an instant best seller that, along with his powerful oratory, had made him a celebrity in the growing abolition movement. No sooner had he arrived in Britain, however, than Douglass began to realize that white abolitionists in Boston had been working to undermine him: Before he’d even left American shores, they had privately written his British hosts and impugned his motives and character. Angela
Angela