Hans Kundnani at The Guardian:
 Many “pro-Europeans” – that is, supporters of European integration or the “European project” in its current form – imagine that the European Union is an expression of cosmopolitanism. They think it stands for diversity, inclusion and openness. It opposes nationalism and racism. It is about people “coming together” and peacefully cooperating. It is a shining example of how enemies can become partners and how diversity can be reconciled with unity.
Many “pro-Europeans” – that is, supporters of European integration or the “European project” in its current form – imagine that the European Union is an expression of cosmopolitanism. They think it stands for diversity, inclusion and openness. It opposes nationalism and racism. It is about people “coming together” and peacefully cooperating. It is a shining example of how enemies can become partners and how diversity can be reconciled with unity.
As the European Commission president José Manuel Barroso put it when the EU was awarded the Nobel Peace prize in 2012 as it struggled to deal with the Eurozone crisis, the European project has shown “that it is possible for peoples and nations to come together across borders” and “that it is possible to overcome the differences between ‘them’ and ‘us’.”
However, there is something rather Eurocentric in thinking of the EU in this way. In particular, by generalising about “peoples and nations” in the way Barroso does, it mistakes Europe for the world.
More here.

 Consciousness presents a “hard problem” to scholars. At stake is how the physical body gives rise to subjective experience. Why consciousness is “hard”, however, is uncertain. One possibility is that the challenge arises from ontology—because consciousness is a special property/substance that is irreducible to the physical. Here, I show how the “hard problem” emerges from two intuitive biases that lie deep within human psychology: Essentialism and Dualism. To determine whether a subjective experience is transformative, people judge whether the experience pertains to one’s essence, and per Essentialism, one’s essence lies within one’s body. Psychological states that seem embodied (e.g., “color vision” ∼ eyes) can thus give rise to transformative experience. Per intuitive Dualism, however, the mind is distinct from the body, and epistemic states (knowledge and beliefs) seem particularly ethereal. It follows that conscious perception (e.g., “seeing color”) ought to seem more transformative than conscious knowledge (e.g., knowledge of how color vision works). Critically, the transformation arises precisely because the conscious perceptual experience seems readily embodied (rather than distinct from the physical body, as the ontological account suggests). In line with this proposal, five experiments show that, in laypeople’s view (a) experience is transformative only when it seems anchored in the human body; (b) gaining a transformative experience effects a bodily change; and (c) the magnitude of the transformation correlates with both (i) the perceived embodiment of that experience, and (ii) with Dualist intuitions, generally. These results cannot solve the ontological question of whether consciousness is distinct from the physical. But they do suggest that the roots of the “hard problem” are partly psychological.
Consciousness presents a “hard problem” to scholars. At stake is how the physical body gives rise to subjective experience. Why consciousness is “hard”, however, is uncertain. One possibility is that the challenge arises from ontology—because consciousness is a special property/substance that is irreducible to the physical. Here, I show how the “hard problem” emerges from two intuitive biases that lie deep within human psychology: Essentialism and Dualism. To determine whether a subjective experience is transformative, people judge whether the experience pertains to one’s essence, and per Essentialism, one’s essence lies within one’s body. Psychological states that seem embodied (e.g., “color vision” ∼ eyes) can thus give rise to transformative experience. Per intuitive Dualism, however, the mind is distinct from the body, and epistemic states (knowledge and beliefs) seem particularly ethereal. It follows that conscious perception (e.g., “seeing color”) ought to seem more transformative than conscious knowledge (e.g., knowledge of how color vision works). Critically, the transformation arises precisely because the conscious perceptual experience seems readily embodied (rather than distinct from the physical body, as the ontological account suggests). In line with this proposal, five experiments show that, in laypeople’s view (a) experience is transformative only when it seems anchored in the human body; (b) gaining a transformative experience effects a bodily change; and (c) the magnitude of the transformation correlates with both (i) the perceived embodiment of that experience, and (ii) with Dualist intuitions, generally. These results cannot solve the ontological question of whether consciousness is distinct from the physical. But they do suggest that the roots of the “hard problem” are partly psychological. Every organism responds to the world with an intricate cascade of biochemistry. There’s a source of heat here, a faint scent of food there, or the crack of a twig as something moves nearby. Each stimulus can trigger the rise of one set of molecules in an animal’s body and perhaps the fall of others. The effect ramifies, tripping feedback loops and flipping switches, until a bird leaps into the air or a bee alights on a flower. It’s a vision of biology that entranced
Every organism responds to the world with an intricate cascade of biochemistry. There’s a source of heat here, a faint scent of food there, or the crack of a twig as something moves nearby. Each stimulus can trigger the rise of one set of molecules in an animal’s body and perhaps the fall of others. The effect ramifies, tripping feedback loops and flipping switches, until a bird leaps into the air or a bee alights on a flower. It’s a vision of biology that entranced  Elon Musk
Elon Musk Last month, in the crowded back room of a bar in Williamsburg, Brooklyn, the fate of humanity hung in the balance.
Last month, in the crowded back room of a bar in Williamsburg, Brooklyn, the fate of humanity hung in the balance. Michaels is intimately acquainted with this power, having spent the last half-century using SNL to launch bankable talents and profit from their careers. Bupkis isn’t just a Pete Davidson vehicle; it’s a Lorne Michaels production. So is Staten Island Summer, for that matter, and Shrill, The Tonight Show, Schmigadoon!, and That Damn Michael Che—not to mention the recently departed The Other Two and Kenan. The promise of SNL under Michaels’ leadership is simple: If you are loyal to the family, you will reap handsome rewards. Over almost 50 years, that promise has come to justify a legacy of alleged workplace abuses ranging from the familiar to the shocking. Beyond 30 Rock’s walls, it has become the promise of the massive live comedy ecosystem feeding SNL, an amorphous network of small businesses that successfully encoded their exploitative labor practices and regressive cultural norms into the industry’s DNA. As they churned ruthlessly through generations of comedy workers, they helped create the world we’re in now, the one Hollywood writers and actors are striking to change. It’s a world where talent and hard work aren’t nearly enough to earn a stable living; a world where a few fabulously wealthy men hold the power to shape entire art forms in their image.
Michaels is intimately acquainted with this power, having spent the last half-century using SNL to launch bankable talents and profit from their careers. Bupkis isn’t just a Pete Davidson vehicle; it’s a Lorne Michaels production. So is Staten Island Summer, for that matter, and Shrill, The Tonight Show, Schmigadoon!, and That Damn Michael Che—not to mention the recently departed The Other Two and Kenan. The promise of SNL under Michaels’ leadership is simple: If you are loyal to the family, you will reap handsome rewards. Over almost 50 years, that promise has come to justify a legacy of alleged workplace abuses ranging from the familiar to the shocking. Beyond 30 Rock’s walls, it has become the promise of the massive live comedy ecosystem feeding SNL, an amorphous network of small businesses that successfully encoded their exploitative labor practices and regressive cultural norms into the industry’s DNA. As they churned ruthlessly through generations of comedy workers, they helped create the world we’re in now, the one Hollywood writers and actors are striking to change. It’s a world where talent and hard work aren’t nearly enough to earn a stable living; a world where a few fabulously wealthy men hold the power to shape entire art forms in their image. A useful tool from Harvard’s Growth Lab:
A useful tool from Harvard’s Growth Lab: J. Howard Rosier interviews Adam Shatz about solidarity, the art of the essay, and his recent collection Writers and Missionaries in The Nation:
J. Howard Rosier interviews Adam Shatz about solidarity, the art of the essay, and his recent collection Writers and Missionaries in The Nation: Branko Milanovic over at his Substack:
Branko Milanovic over at his Substack: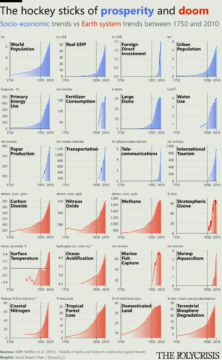
 Do you know what makes you attractive? Your best features are the
Do you know what makes you attractive? Your best features are the  We could all use a hype man like George Henry Lewes.
We could all use a hype man like George Henry Lewes. “A
“A While recent events have provided a painful reminder of the very bad viruses that prey on us, Tom Ireland’s “The Good Virus” is a colorful redemption story for the oft-neglected yet incredibly abundant phage, and its potential for quelling the existential threat of antibiotic resistance, which scientists estimate might cause up to 10 million deaths per year by 2050. Ireland, an award-winning science journalist, approaches the subject of his first book with curiosity and passion, delivering a deft narrative that is rich and approachable.
While recent events have provided a painful reminder of the very bad viruses that prey on us, Tom Ireland’s “The Good Virus” is a colorful redemption story for the oft-neglected yet incredibly abundant phage, and its potential for quelling the existential threat of antibiotic resistance, which scientists estimate might cause up to 10 million deaths per year by 2050. Ireland, an award-winning science journalist, approaches the subject of his first book with curiosity and passion, delivering a deft narrative that is rich and approachable.