 Henry Farrell and Abraham L. Newman in Foreign Affairs:
Henry Farrell and Abraham L. Newman in Foreign Affairs:
[Thomas] Friedman was right that a globalized world had arrived but wrong about what that world would look like. Instead of liberating governments and businesses, globalization entangled them. As digital networks, financial flows, and supply chains stretched across the globe, states—especially the United States—started treating them as webs in which to trap one another. Today, the U.S. National Security Agency lurks at the heart of the Internet, listening in on all kinds of communications. The U.S. Department of the Treasury uses the international financial system to punish rogue states and errant financial institutions. In service of its trade war with China, Washington has tied down massive firms and entire national economies by targeting vulnerable points in global supply chains. Other countries are in on the game, too: Japan has used its control over key industrial chemicals to hold South Korea’s electronics industry for ransom, and Beijing might eventually be able to infiltrate the world’s 5G communications system through its access to the Chinese telecommunications giant Huawei.
Globalization, in short, has proved to be not a force for liberation but a new source of vulnerability, competition, and control; networks have proved to be less paths to freedom than new sets of chains. Governments and societies, however, have come to understand this reality far too late to reverse it. In the past few years, Beijing and Washington have been just the most visible examples of governments recognizing how many dangers come with interdependence and frantically trying to do something about it. But the economies of countries such as China and the United States are too deeply entwined to be separated—or “decoupled”—without causing chaos.

 In the years before a woman becomes a writer, the rooms are never her own, and that can be a very fine thing. Decades before receiving the Baudelairian authorship, when she first moved to Paris as a young woman, Hazel Brown stayed in cheap hotels, admiring the neutrality of spaces designed for everyone and no one: “No judgment, no need, no contract, no seduction: just the free promiscuity of a disrobed mind.” She thereafter sublets teensy, humble apartments, living alongside the unremarkable belongings of people she doesn’t know—an actress (a role-player), a graphologist (a handwriting analyst). She spends her days reading in the park, filling her head with the words of others, of people she also doesn’t know, and picking up boys to kiss and fuck. She is equally enamored of sex and sentences; each, sensual and electrifying, grazes her body, at once possessing it and proving its otherness. She takes menial jobs: one at the summer house of a convalescing widow, for whom she performs all manner of household duties; later, she’s hired to mind the daughter of a wealthy couple, shuttling her from school back to their apartment, where Hazel Brown does the ironing and dusting, playing proxy for the wife and mother who recently returned to work.
In the years before a woman becomes a writer, the rooms are never her own, and that can be a very fine thing. Decades before receiving the Baudelairian authorship, when she first moved to Paris as a young woman, Hazel Brown stayed in cheap hotels, admiring the neutrality of spaces designed for everyone and no one: “No judgment, no need, no contract, no seduction: just the free promiscuity of a disrobed mind.” She thereafter sublets teensy, humble apartments, living alongside the unremarkable belongings of people she doesn’t know—an actress (a role-player), a graphologist (a handwriting analyst). She spends her days reading in the park, filling her head with the words of others, of people she also doesn’t know, and picking up boys to kiss and fuck. She is equally enamored of sex and sentences; each, sensual and electrifying, grazes her body, at once possessing it and proving its otherness. She takes menial jobs: one at the summer house of a convalescing widow, for whom she performs all manner of household duties; later, she’s hired to mind the daughter of a wealthy couple, shuttling her from school back to their apartment, where Hazel Brown does the ironing and dusting, playing proxy for the wife and mother who recently returned to work. Of all the ill-fated revolutions of the
Of all the ill-fated revolutions of the  Modern recycling as we know it—the byzantine system of color-coded bins and asterisk-ridden instruction sheets about what is or isn’t “recyclable”—was conceived in a boardroom. The anti-litter campaigns of the 1950s, championed under the slogan of “Keep America Beautiful,” were funded by the producers of that litter, who sought to position recycling as a viable alternative to the sustainable packaging laws that had percolated in nearly two dozen states. In primetime commercials over the decades, American audiences met characters like Susan Spotless and “The Crying Indian” (played by Italian-American actor Espera Oscar de Corti) who urged consumers to lead the charge against debris: “People start pollution. People can stop it.”
Modern recycling as we know it—the byzantine system of color-coded bins and asterisk-ridden instruction sheets about what is or isn’t “recyclable”—was conceived in a boardroom. The anti-litter campaigns of the 1950s, championed under the slogan of “Keep America Beautiful,” were funded by the producers of that litter, who sought to position recycling as a viable alternative to the sustainable packaging laws that had percolated in nearly two dozen states. In primetime commercials over the decades, American audiences met characters like Susan Spotless and “The Crying Indian” (played by Italian-American actor Espera Oscar de Corti) who urged consumers to lead the charge against debris: “People start pollution. People can stop it.” SYNTHETIC BIOLOGY,
SYNTHETIC BIOLOGY, Virginia Woolf, aged 23, recently orphaned and still 10 years away from publishing her debut novel, was first commissioned to write reviews for the TLS in 1905. She began, as Francesca Wade points out in her preface to this collection, like any novice – by reviewing anything the editors sent her: guide books, cookery books, poetry, debut novels. Often she was filing a piece a week, reading the book on Sunday, writing – in the anonymous, authoritative
Virginia Woolf, aged 23, recently orphaned and still 10 years away from publishing her debut novel, was first commissioned to write reviews for the TLS in 1905. She began, as Francesca Wade points out in her preface to this collection, like any novice – by reviewing anything the editors sent her: guide books, cookery books, poetry, debut novels. Often she was filing a piece a week, reading the book on Sunday, writing – in the anonymous, authoritative  For at least a decade now there’s been a buzz about Mark Bradford. People call him an exciting painter. Those two words, “exciting” and “painting,” don’t get put together very often, which is understandable. There is something about painting that promotes a reflective attitude. You look at a painting by standing your distance and contemplating. You can like a painting, love a painting, even be moved by a painting. But excitement? Not so much. What is it about Bradford’s paintings that makes them exciting? The answer, I think, is that Bradford has discovered an approach to abstraction that’s genuinely fresh, genuinely new. No one’s done it quite like this before.
For at least a decade now there’s been a buzz about Mark Bradford. People call him an exciting painter. Those two words, “exciting” and “painting,” don’t get put together very often, which is understandable. There is something about painting that promotes a reflective attitude. You look at a painting by standing your distance and contemplating. You can like a painting, love a painting, even be moved by a painting. But excitement? Not so much. What is it about Bradford’s paintings that makes them exciting? The answer, I think, is that Bradford has discovered an approach to abstraction that’s genuinely fresh, genuinely new. No one’s done it quite like this before. A large number of well done studies have painted a rather consistent picture of sex differences in personality that are strikingly consistent across cultures (see
A large number of well done studies have painted a rather consistent picture of sex differences in personality that are strikingly consistent across cultures (see  Benton was massively popular in his heyday. This Is My Beloved came out in 1943; Billboard reported in early 1949 that the book had sold more than 350,000 copies, and it remained continuously in print for decades. Benton’s work appeared in the Yale Review, Esquire, the New Republic, Poetry, and other prestigious outlets, but he’s best remembered today (if at all) for his World War II poetry. The only contemporary review of This Is My Beloved I could track down was in Kirkus Reviews in 1942. It’s a wry, saucy write-up that reads: “High voltage verse, this, in free verse for a sequence of lyrics commemorating a love affair and its termination. Intimate corporeal and physical detail and extravagant praise thereof, in what might mildly be termed erotica.
Benton was massively popular in his heyday. This Is My Beloved came out in 1943; Billboard reported in early 1949 that the book had sold more than 350,000 copies, and it remained continuously in print for decades. Benton’s work appeared in the Yale Review, Esquire, the New Republic, Poetry, and other prestigious outlets, but he’s best remembered today (if at all) for his World War II poetry. The only contemporary review of This Is My Beloved I could track down was in Kirkus Reviews in 1942. It’s a wry, saucy write-up that reads: “High voltage verse, this, in free verse for a sequence of lyrics commemorating a love affair and its termination. Intimate corporeal and physical detail and extravagant praise thereof, in what might mildly be termed erotica.  When I was a child, there was a book about the Polish artist Balthus in the small library at our country home. It was dad’s book, big and heavy. The skin between my thumb and index finger stretched taut when I took it down from the shelf. Sometimes I would sit at the table there in the library and page through the book. The table was by a window that looked out on a forest of firs. The light from the window was dim and pale; it seemed to lack strength and direction.
When I was a child, there was a book about the Polish artist Balthus in the small library at our country home. It was dad’s book, big and heavy. The skin between my thumb and index finger stretched taut when I took it down from the shelf. Sometimes I would sit at the table there in the library and page through the book. The table was by a window that looked out on a forest of firs. The light from the window was dim and pale; it seemed to lack strength and direction. When Guy Partnerman and Lady Millionaire purchased a brownstone in the most Brooklyn-themed neighborhood of Brooklyn, there was only one drawback: the home was too beautiful.
When Guy Partnerman and Lady Millionaire purchased a brownstone in the most Brooklyn-themed neighborhood of Brooklyn, there was only one drawback: the home was too beautiful.

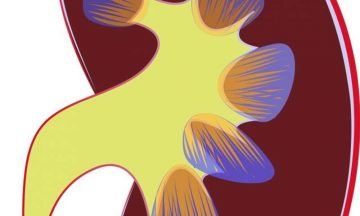 p53 is the most famous cancer gene, not least because it’s involved in causing over 50% of all cancers. When a cell loses its p53 gene—when the gene becomes mutated—it unleashes many processes that lead to the uncontrolled cell growth and refusal to die, which are hallmarks of cancer growth. But there are some cancers, like kidney cancer, that that had few p53 mutations. In order to understand whether the inactivation of the p53 pathway might contribute to kidney cancer development, Haifang Yang, Ph.D., a researcher with the Sidney Kimmel Cancer Center—Jefferson Health probed kidney cancer’s genes for interactions with p53.
p53 is the most famous cancer gene, not least because it’s involved in causing over 50% of all cancers. When a cell loses its p53 gene—when the gene becomes mutated—it unleashes many processes that lead to the uncontrolled cell growth and refusal to die, which are hallmarks of cancer growth. But there are some cancers, like kidney cancer, that that had few p53 mutations. In order to understand whether the inactivation of the p53 pathway might contribute to kidney cancer development, Haifang Yang, Ph.D., a researcher with the Sidney Kimmel Cancer Center—Jefferson Health probed kidney cancer’s genes for interactions with p53. Humans boast a rich trove of words to express the way we feel. Some are not easily translatable between languages: Germans use “Weltschmerz” to refer to a feeling of melancholy caused by the state of the world. And the indigenous Baining people of Papua New Guinea say “awumbuk” to describe a social hangover that leaves people unmotivated and listless for days after the departure of overnight guests. Other terms seem rather common—“fear,” for example, translates to “takot” in Tagalog and “ótti” in Icelandic. These similarities and differences raise a question: Does the way we experience emotions cross cultural boundaries?
Humans boast a rich trove of words to express the way we feel. Some are not easily translatable between languages: Germans use “Weltschmerz” to refer to a feeling of melancholy caused by the state of the world. And the indigenous Baining people of Papua New Guinea say “awumbuk” to describe a social hangover that leaves people unmotivated and listless for days after the departure of overnight guests. Other terms seem rather common—“fear,” for example, translates to “takot” in Tagalog and “ótti” in Icelandic. These similarities and differences raise a question: Does the way we experience emotions cross cultural boundaries? In Not Enough, Samuel Moyn addresses a disjunction between the language of human rights and the facts of inequality. Our unequal world, Moyn observes, is one in which the rich have grown ever richer, but the poor have remained poor, or, at best, not quite as poor as they once were. The language of human rights may not have been the cause of economic inequality, he argues, but neither has it done much to prevent it. Moyn, a professor of law and history at Yale University, draws upon a wide range of sources in making his claims: nineteenth-century debates about distributive ethics, eighteenth-century Jacobin texts and treatises, medieval and ancient sources. Moyn also considers more recent events that have long been associated with the history of human rights: Franklin D. Roosevelt’s Second Bill of Rights; the Universal Declaration of Human Rights; and later efforts to emphasize material equality and social justice in the context of decolonization. These efforts, Moyn believes, were too easily assimilated in welfare states, or outpaced in others. They converted none to the cause.
In Not Enough, Samuel Moyn addresses a disjunction between the language of human rights and the facts of inequality. Our unequal world, Moyn observes, is one in which the rich have grown ever richer, but the poor have remained poor, or, at best, not quite as poor as they once were. The language of human rights may not have been the cause of economic inequality, he argues, but neither has it done much to prevent it. Moyn, a professor of law and history at Yale University, draws upon a wide range of sources in making his claims: nineteenth-century debates about distributive ethics, eighteenth-century Jacobin texts and treatises, medieval and ancient sources. Moyn also considers more recent events that have long been associated with the history of human rights: Franklin D. Roosevelt’s Second Bill of Rights; the Universal Declaration of Human Rights; and later efforts to emphasize material equality and social justice in the context of decolonization. These efforts, Moyn believes, were too easily assimilated in welfare states, or outpaced in others. They converted none to the cause. Twenty-six years into the war, a harsh assessment
Twenty-six years into the war, a harsh assessment  In January 2018, Russia secretly launched a cruise missile powered by a small nuclear reactor at a military testing range in the northern region of Arkhangelsk. The test of this bizarre doomsday weapon was a failure—it landed in the sea just a few kilometres from the launch site. The test would have remained a secret, but in August 2019 Russian scientists attempted to lift the wreckage off the Arctic seafloor. There was an explosion—one powerful enough to be detected by monitoring stations in Finland, Norway and Sweden. Five scientists were killed and a brief spike of radiation was detected in the nearby city of Severodvinsk. Images on social media showed emergency service workers responding in Hazmat suits. The Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban treaty Organisation, the body charged with detecting nuclear explosions, predicted that any plume of radionuclides from the accident would soon drift over monitoring stations in central Russia. Then those stations mysteriously stopped working. Viewers of the drama series Chernobyl might not have been surprised.
In January 2018, Russia secretly launched a cruise missile powered by a small nuclear reactor at a military testing range in the northern region of Arkhangelsk. The test of this bizarre doomsday weapon was a failure—it landed in the sea just a few kilometres from the launch site. The test would have remained a secret, but in August 2019 Russian scientists attempted to lift the wreckage off the Arctic seafloor. There was an explosion—one powerful enough to be detected by monitoring stations in Finland, Norway and Sweden. Five scientists were killed and a brief spike of radiation was detected in the nearby city of Severodvinsk. Images on social media showed emergency service workers responding in Hazmat suits. The Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban treaty Organisation, the body charged with detecting nuclear explosions, predicted that any plume of radionuclides from the accident would soon drift over monitoring stations in central Russia. Then those stations mysteriously stopped working. Viewers of the drama series Chernobyl might not have been surprised.