Maria Popova at Brain Pickings:
 Despite her precocity and her early determination, it took Somerville half a lifetime to come abloom as a scientist — the spring and summer of her life passed with her genius laying restive beneath the frost of the era’s receptivity to the female mind. When Somerville was forty-six, she published her first scientific paper — a study of the magnetic properties of violet rays — which earned her praise from the inventor of the kaleidoscope, Sir David Brewster, as “the most extraordinary woman in Europe — a mathematician of the very first rank with all the gentleness of a woman.” Lord Brougham, the influential founder of the newly established Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge — with which Thoreau would take issue thirty-some years later by making a case for “the diffusion of useful ignorance,” comprising “knowledge useful in a higher sense” — was so impressed that he asked Somerville to translate a mathematical treatise by Pierre-Simon Laplace, “the Newton of France.” She took the project on, perhaps not fully aware how many years it would take to complete to her satisfaction, which would forever raise the common standard of excellence. All great works suffer from and are saved by a gladsome blindness to what they ultimately demand of their creators.
Despite her precocity and her early determination, it took Somerville half a lifetime to come abloom as a scientist — the spring and summer of her life passed with her genius laying restive beneath the frost of the era’s receptivity to the female mind. When Somerville was forty-six, she published her first scientific paper — a study of the magnetic properties of violet rays — which earned her praise from the inventor of the kaleidoscope, Sir David Brewster, as “the most extraordinary woman in Europe — a mathematician of the very first rank with all the gentleness of a woman.” Lord Brougham, the influential founder of the newly established Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge — with which Thoreau would take issue thirty-some years later by making a case for “the diffusion of useful ignorance,” comprising “knowledge useful in a higher sense” — was so impressed that he asked Somerville to translate a mathematical treatise by Pierre-Simon Laplace, “the Newton of France.” She took the project on, perhaps not fully aware how many years it would take to complete to her satisfaction, which would forever raise the common standard of excellence. All great works suffer from and are saved by a gladsome blindness to what they ultimately demand of their creators.
more here.

 A direct line runs between the vibrant, colorful, and earthy diction of canting to cockney rhyming slang, or the endangered dialect of Polari used for decades by gay men in Great Britain, who lived under the constant threat of state punishment. All of these tongues are “obscene,” but that’s a function of their oppositional status to received language. Nothing is “dirty” about them; they are, rather, rebellions against “proper” speech, “dignified” language, “correct” talking, and they challenge that codified violence implied by the mere existence of the King’s Speech. Their differing purposes, and respective class connotations and authenticity, are illustrated by a joke wherein a hobo asks a nattily dressed businessman for some change. “’Neither a borrower nor a lender be’—that’s William Shakespeare,” says the businessman. “’Fuck you’—that’s David Mamet,” responds the panhandler. A bit of a disservice to the Bard, however, who along with Dekker and Middleton could cant with the best of them. For example, within the folio one will find “bawling, blasphemous, incharitible dog,” “paper fac’d villain,” and “embossed carbuncle,” among such other similarly colorful examples.
A direct line runs between the vibrant, colorful, and earthy diction of canting to cockney rhyming slang, or the endangered dialect of Polari used for decades by gay men in Great Britain, who lived under the constant threat of state punishment. All of these tongues are “obscene,” but that’s a function of their oppositional status to received language. Nothing is “dirty” about them; they are, rather, rebellions against “proper” speech, “dignified” language, “correct” talking, and they challenge that codified violence implied by the mere existence of the King’s Speech. Their differing purposes, and respective class connotations and authenticity, are illustrated by a joke wherein a hobo asks a nattily dressed businessman for some change. “’Neither a borrower nor a lender be’—that’s William Shakespeare,” says the businessman. “’Fuck you’—that’s David Mamet,” responds the panhandler. A bit of a disservice to the Bard, however, who along with Dekker and Middleton could cant with the best of them. For example, within the folio one will find “bawling, blasphemous, incharitible dog,” “paper fac’d villain,” and “embossed carbuncle,” among such other similarly colorful examples. There’s really nothing in
There’s really nothing in 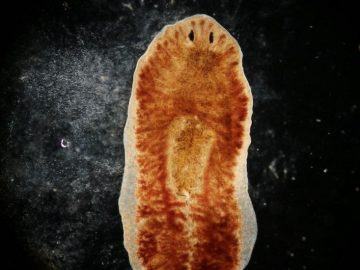 The study of memory has always been one of the stranger outposts of science. In the 1950s, an unknown psychology professor at the University of Michigan named James McConnell made headlines—and eventually became something of a
The study of memory has always been one of the stranger outposts of science. In the 1950s, an unknown psychology professor at the University of Michigan named James McConnell made headlines—and eventually became something of a  You will recall that while I carried on and on about myself in
You will recall that while I carried on and on about myself in  The blob is a cloud of turbulence in a large water tank in the lab of the University of Chicago physicist
The blob is a cloud of turbulence in a large water tank in the lab of the University of Chicago physicist  The global pandemic has re-written the rules of global macroeconomic policy for us. We have witnessed significant monetary and fiscal policy innovation; growing unwillingness to accept that the design of stimulus should be independent of broader environmental and social goals; and a far more acute focus on the competence and scope of the State.
The global pandemic has re-written the rules of global macroeconomic policy for us. We have witnessed significant monetary and fiscal policy innovation; growing unwillingness to accept that the design of stimulus should be independent of broader environmental and social goals; and a far more acute focus on the competence and scope of the State. Will we be surprised again this November the way Americans were on Nov. 9, 2016 when they awoke to learn that reality TV star Donald Trump had been elected president? That outcome defied prognosticators and polls, and even Trump’s own expectation. “Oh, this is gonna be embarrassing,”
Will we be surprised again this November the way Americans were on Nov. 9, 2016 when they awoke to learn that reality TV star Donald Trump had been elected president? That outcome defied prognosticators and polls, and even Trump’s own expectation. “Oh, this is gonna be embarrassing,”  Arundhati Roy’s literary career has been one of a kind. Thrust into the limelight of the global publishing industry back in 1997 when her debut novel,
Arundhati Roy’s literary career has been one of a kind. Thrust into the limelight of the global publishing industry back in 1997 when her debut novel,  Urban Legends is a parabolic dish microphone pointed at history, collecting the waves that outsiders have bounced off the South Bronx. L’Official gathers representations of the South Bronx found in fiction, like Don DeLillo’s description of urban tourism in Underworld, and the ways it has been filtered through journalistic language. He proposes that classifications like “inner city” and the “ghetto” are also “versions of urban legends as well.” L’Official presents these ideas as euphemisms and “coded spatial signifiers for race,” which they are. In fact, the focus of Urban Legends is squarely on the views of those who never lived in the neighborhood. Very little of it touches on how the residents of the South Bronx represented themselves, and L’Official acknowledges this several times, best of all in the conclusion: “Though Urban Legends falls short of discussing ‘all kinds’ of artists, its aims were, and are, aligned with those of the Fort Apache Band, as articulated by Andy González: showing that art can, and does, emerge from an imperiled environment.” L’Official seems to know that hip-hop and graffiti don’t need his help at this point. He writes that graffiti artists in the South Bronx—“most of whom pointedly referred to themselves as writers—would no doubt tell you, graffiti was Bronx literature, and a populist form at that, which hardly required an agent or a publishing contract to reach an audience.”
Urban Legends is a parabolic dish microphone pointed at history, collecting the waves that outsiders have bounced off the South Bronx. L’Official gathers representations of the South Bronx found in fiction, like Don DeLillo’s description of urban tourism in Underworld, and the ways it has been filtered through journalistic language. He proposes that classifications like “inner city” and the “ghetto” are also “versions of urban legends as well.” L’Official presents these ideas as euphemisms and “coded spatial signifiers for race,” which they are. In fact, the focus of Urban Legends is squarely on the views of those who never lived in the neighborhood. Very little of it touches on how the residents of the South Bronx represented themselves, and L’Official acknowledges this several times, best of all in the conclusion: “Though Urban Legends falls short of discussing ‘all kinds’ of artists, its aims were, and are, aligned with those of the Fort Apache Band, as articulated by Andy González: showing that art can, and does, emerge from an imperiled environment.” L’Official seems to know that hip-hop and graffiti don’t need his help at this point. He writes that graffiti artists in the South Bronx—“most of whom pointedly referred to themselves as writers—would no doubt tell you, graffiti was Bronx literature, and a populist form at that, which hardly required an agent or a publishing contract to reach an audience.” IN HER 2007 BOOK, Awkward: A Detour, Mary Cappello posits the title state as a natural response to a world indifferent to our comfort or desires. “Awkwardness could be an effect of the rough handling of reality over which one has no control,” she proposes, and over the course of her wide-ranging, digressive, book-length essay, Cappello approaches the question of awkwardness from a variety of different angles. Melding memoir, literary and film criticism, etymological study, and many other modes, her book offers up a range of perspectives on and definitions of the state of awkwardness, all of which speak to the gap between our natural inclinations and the ways we are forced to adjust these inclinations to fit both a physical world and a social environment that routinely refutes them. “Each day on earth,” Cappello writes, “is at base an endless adjustment to there being too much or not enough, to there being something missing or something extra,” and it’s in this adjustment that awkwardness occurs.
IN HER 2007 BOOK, Awkward: A Detour, Mary Cappello posits the title state as a natural response to a world indifferent to our comfort or desires. “Awkwardness could be an effect of the rough handling of reality over which one has no control,” she proposes, and over the course of her wide-ranging, digressive, book-length essay, Cappello approaches the question of awkwardness from a variety of different angles. Melding memoir, literary and film criticism, etymological study, and many other modes, her book offers up a range of perspectives on and definitions of the state of awkwardness, all of which speak to the gap between our natural inclinations and the ways we are forced to adjust these inclinations to fit both a physical world and a social environment that routinely refutes them. “Each day on earth,” Cappello writes, “is at base an endless adjustment to there being too much or not enough, to there being something missing or something extra,” and it’s in this adjustment that awkwardness occurs. There are two dead babies sitting in a medical pan inside a nondescript room. These babies face one another. Are they conjoined twins? There are tubes connected to the twin cadavers. A Chinese couple, a man and a woman, sit in chairs on either side of the babies. The tubes from the babies are connected to the arms of the couple. They are feeding their own blood into the mouths of the dead babies, who receive the elixir without discernible effect as the blood dribbles down their faces. It is a horrendous scene, made all the more horrendous by the fact that it is so compelling to look at, so fascinating to think about. Are these people trying to help the babies, connect with them somehow? Are they making fun of these dead babies or of the situation? Are we meant to laugh, cry, recoil in horror? What is this disturbing scene and why are we being subjected to it?
There are two dead babies sitting in a medical pan inside a nondescript room. These babies face one another. Are they conjoined twins? There are tubes connected to the twin cadavers. A Chinese couple, a man and a woman, sit in chairs on either side of the babies. The tubes from the babies are connected to the arms of the couple. They are feeding their own blood into the mouths of the dead babies, who receive the elixir without discernible effect as the blood dribbles down their faces. It is a horrendous scene, made all the more horrendous by the fact that it is so compelling to look at, so fascinating to think about. Are these people trying to help the babies, connect with them somehow? Are they making fun of these dead babies or of the situation? Are we meant to laugh, cry, recoil in horror? What is this disturbing scene and why are we being subjected to it? In the service of seeking truth, there would seem to be value in intellectual diversity, both in keeping ourselves honest and in the possibility of new ideas coming from unexpected quarters. That’s true in the natural sciences, but even more so in the humanities and social sciences, where the right/wrong distinction is sometimes less clear. But academia isn’t always diverse; as an empirical fact, there are a lot more liberals on university faculties than there are conservatives. I talk with Musa al-Gharbi about why this is true — self-selection? discrimination? — the extent to which it’s a real problem, and how we should better think about the value of diverse viewpoints.
In the service of seeking truth, there would seem to be value in intellectual diversity, both in keeping ourselves honest and in the possibility of new ideas coming from unexpected quarters. That’s true in the natural sciences, but even more so in the humanities and social sciences, where the right/wrong distinction is sometimes less clear. But academia isn’t always diverse; as an empirical fact, there are a lot more liberals on university faculties than there are conservatives. I talk with Musa al-Gharbi about why this is true — self-selection? discrimination? — the extent to which it’s a real problem, and how we should better think about the value of diverse viewpoints. At 7:47 a.m. on the Sunday of Memorial Day weekend, Dr. Jay Butler pounded out a grim email to colleagues at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta.
At 7:47 a.m. on the Sunday of Memorial Day weekend, Dr. Jay Butler pounded out a grim email to colleagues at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta.