Courtney Connley in Make it:
 Black Americans have played a crucial role in helping to advance America’s business, political and cultural landscape into what it is today. And since 1976, every U.S. president has designated the month of February as Black History Month to honor the achievements and the resilience of the Black community. While CNBC Make It recognizes that Black history is worth being celebrated year-round, we are using this February to shine a special spotlight on 23 Black leaders whose recent accomplishments and impact will inspire many generations to come. These leaders, who have made history in their respective fields, stand on the shoulders of pioneers who came before them, including Shirley Chisholm, John Lewis, Maya Angelou and Mary Ellen Pleasant.
Black Americans have played a crucial role in helping to advance America’s business, political and cultural landscape into what it is today. And since 1976, every U.S. president has designated the month of February as Black History Month to honor the achievements and the resilience of the Black community. While CNBC Make It recognizes that Black history is worth being celebrated year-round, we are using this February to shine a special spotlight on 23 Black leaders whose recent accomplishments and impact will inspire many generations to come. These leaders, who have made history in their respective fields, stand on the shoulders of pioneers who came before them, including Shirley Chisholm, John Lewis, Maya Angelou and Mary Ellen Pleasant.
Following the lead of trailblazers throughout American history, today’s Black history-makers are shaping not only today but tomorrow. From helping to develop a Covid-19 vaccine, to breaking barriers in the White House and in the C-suite, below are 23 Black leaders who are shattering glass ceilings in their wide-ranging roles.
More here. (Throughout February, at least one post will be dedicated to honoring Black History Month. The theme this year is: The Family)

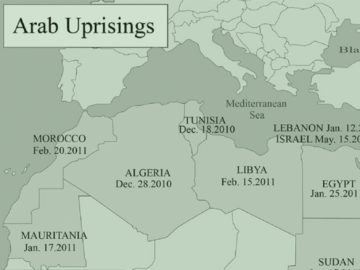 It is in the middle of winter that the “Arab Spring” comes unexpectedly. On December 17, 2010, in Sidi Bouzid, an agricultural village in central Tunisia, Mohamed Bouazizi, a young unemployed peddler, sets himself on fire after his merchandise is confiscated by police officers. The day after the tragedy, the anger spreads to other cities in the country. President Zine el-Abidine Ben Ali, who has been in power for twenty-three years, denounces “terrorist acts” perpetrated by “hooded thugs.” The deaths will soon be counted by the dozens during clashes with the forces of law and order. “Irhal!” (“leave”) becomes the revolution’s byword. Ben Ali is accused not only of having established a police regime, but also of pillaging Tunisia. On January 14, 2011, overwhelmed by the events, he flees with his family to Saudi Arabia.
It is in the middle of winter that the “Arab Spring” comes unexpectedly. On December 17, 2010, in Sidi Bouzid, an agricultural village in central Tunisia, Mohamed Bouazizi, a young unemployed peddler, sets himself on fire after his merchandise is confiscated by police officers. The day after the tragedy, the anger spreads to other cities in the country. President Zine el-Abidine Ben Ali, who has been in power for twenty-three years, denounces “terrorist acts” perpetrated by “hooded thugs.” The deaths will soon be counted by the dozens during clashes with the forces of law and order. “Irhal!” (“leave”) becomes the revolution’s byword. Ben Ali is accused not only of having established a police regime, but also of pillaging Tunisia. On January 14, 2011, overwhelmed by the events, he flees with his family to Saudi Arabia. It is possible that John Pringle’s neighbors viewed him with some distaste. Formerly physician-general to the British forces in the Low Countries, in 1749 Pringle had settled down in a rather swanky part of London, where he began investigating the processes behind putrefaction. He would place pieces of beef in a lamp furnace, sometimes combining them with another substance — and then wait for putrefaction to commence, or not. Falsifying an earlier hypothesis, Pringle showed that not only acids but alkalis, like baker’s ammonia, could retard the progress of decay. Even more impressively, some substances, like Peruvian bark (source of the malarial prophylactic, quinine) could outright reverse putrefaction, rendering tainted meat seemingly edible again.
It is possible that John Pringle’s neighbors viewed him with some distaste. Formerly physician-general to the British forces in the Low Countries, in 1749 Pringle had settled down in a rather swanky part of London, where he began investigating the processes behind putrefaction. He would place pieces of beef in a lamp furnace, sometimes combining them with another substance — and then wait for putrefaction to commence, or not. Falsifying an earlier hypothesis, Pringle showed that not only acids but alkalis, like baker’s ammonia, could retard the progress of decay. Even more impressively, some substances, like Peruvian bark (source of the malarial prophylactic, quinine) could outright reverse putrefaction, rendering tainted meat seemingly edible again. We live in an era of intersecting crises—some new, some old but newly visible. At the time of writing, the COVID-19 pandemic has already caused nearly 500,000 deaths in the United States alone, with many more deaths on the horizon in the coming months. Since its arrival in the United States, the virus has intersected with and magnified long-neglected problems—radical disparities in access to healthcare and the fulfillment of basic needs that disproportionately impact communities of color and working-class Americans, alongside a crisis of care for the young, elderly, and sick that stretches families and communities to the breaking point.
We live in an era of intersecting crises—some new, some old but newly visible. At the time of writing, the COVID-19 pandemic has already caused nearly 500,000 deaths in the United States alone, with many more deaths on the horizon in the coming months. Since its arrival in the United States, the virus has intersected with and magnified long-neglected problems—radical disparities in access to healthcare and the fulfillment of basic needs that disproportionately impact communities of color and working-class Americans, alongside a crisis of care for the young, elderly, and sick that stretches families and communities to the breaking point. “People under seventy and over seven are very unreliable if they are not cats,” somebody says a few pages into Leonora Carrington’s 1974 novel The Hearing Trumpet. Most people would agree; if anything, the bad run of septuagenarians of late shows this age range is too narrow. The statement is characteristic of this chatoyant novel. Cats are everywhere in The Hearing Trumpet: their sheddings are collected to form a sleeveless cardigan; psychic powers are attributed to them; the earth freezes over and an earthquake thins out the human population, but the cats survive. Beneath its cattiness, the remark also offhandedly conflates species (the way “people” transmutes into “cats” at the end of the sentence) and recognizes the virtue of people usually excluded from civic life for being too young or too old. This broadening out of our ordinary categories of human life is at the heart of the novel.
“People under seventy and over seven are very unreliable if they are not cats,” somebody says a few pages into Leonora Carrington’s 1974 novel The Hearing Trumpet. Most people would agree; if anything, the bad run of septuagenarians of late shows this age range is too narrow. The statement is characteristic of this chatoyant novel. Cats are everywhere in The Hearing Trumpet: their sheddings are collected to form a sleeveless cardigan; psychic powers are attributed to them; the earth freezes over and an earthquake thins out the human population, but the cats survive. Beneath its cattiness, the remark also offhandedly conflates species (the way “people” transmutes into “cats” at the end of the sentence) and recognizes the virtue of people usually excluded from civic life for being too young or too old. This broadening out of our ordinary categories of human life is at the heart of the novel.
 Klara and the Sun asks readers to love a robot and, the funny thing is, we do. This is a novel not just about a machine but narrated by a machine, though the word is not used about her until late in the book when it is wielded by a stranger as an insult. People distrust and then start to like her: “Are you alright, Klara?” Apart from the occasional lapse into bullying or indifference, humans are solicitous of Klara’s feelings – if that is what they are. Klara is built to observe and understand humans, and these actions are so close to empathy they may amount to the same thing. “I believe I have many feelings,” she says. “The more I observe the more feelings become available to me.” Klara is an AF, or artificial friend, who is bought as a companion for 14-year-old Josie, a girl suffering from a mysterious, perhaps terminal illness. Klara is loyal and tactful, she is able to absorb difficulty and return care. Her role, as she describes it, is to prevent loneliness and to serve.
Klara and the Sun asks readers to love a robot and, the funny thing is, we do. This is a novel not just about a machine but narrated by a machine, though the word is not used about her until late in the book when it is wielded by a stranger as an insult. People distrust and then start to like her: “Are you alright, Klara?” Apart from the occasional lapse into bullying or indifference, humans are solicitous of Klara’s feelings – if that is what they are. Klara is built to observe and understand humans, and these actions are so close to empathy they may amount to the same thing. “I believe I have many feelings,” she says. “The more I observe the more feelings become available to me.” Klara is an AF, or artificial friend, who is bought as a companion for 14-year-old Josie, a girl suffering from a mysterious, perhaps terminal illness. Klara is loyal and tactful, she is able to absorb difficulty and return care. Her role, as she describes it, is to prevent loneliness and to serve. Transitional justice is both a legal and philosophical
Transitional justice is both a legal and philosophical  This is the familiar arc that Jonathan Sadowsky traces in his new book The Empire of Depression: A New History. But Sadowsky, a medical historian at Case Western, aims to show how the Western notion of depression is making its way around the globe, threatening to displace other conceptions of the disease. “Western psychiatry often treats anxiety and depression as separate things that often occur together. In many places, though, anxiety and depression are seen as part of one thing,” he writes. And the sense of what causes depression differs significantly, too. Whereas in the West, depression is most often understood as having a physical reason, be it genes, or chemistry, “globally, it is more common to consider depression to be at once psychological, social, and physical.”
This is the familiar arc that Jonathan Sadowsky traces in his new book The Empire of Depression: A New History. But Sadowsky, a medical historian at Case Western, aims to show how the Western notion of depression is making its way around the globe, threatening to displace other conceptions of the disease. “Western psychiatry often treats anxiety and depression as separate things that often occur together. In many places, though, anxiety and depression are seen as part of one thing,” he writes. And the sense of what causes depression differs significantly, too. Whereas in the West, depression is most often understood as having a physical reason, be it genes, or chemistry, “globally, it is more common to consider depression to be at once psychological, social, and physical.” “IMAGINE, IF YOU CAN, a small room, hexagonal in shape, like the cell of a bee.” So begins a story by E. M. Forster from over a century ago, about a future that feels uncannily like our present. Called “The Machine Stops,” the story conjures a world of individual humans isolated in such rooms who pass the time by streaming lectures and videoconferencing as the titular Machine tends to their every need. It is a world in which everything — music, food, even your bed — is summoned by the click of a button. In place of work, the Machine offers material and intellectual sustenance. For the story’s main character, Vashti, it turns life into a reassuringly predictable cycle: “[S]he made the room dark and slept; she awoke and made the room light; she ate and exchanged ideas with her friends, and listened to music and attended lectures; she made the room dark and slept. Above her, beneath her, and around her, the Machine hummed eternally.” To Vashti, the Machine offers serenity and certainty in equal measure. In this imagined world of isolated togetherness, heaven is a place.
“IMAGINE, IF YOU CAN, a small room, hexagonal in shape, like the cell of a bee.” So begins a story by E. M. Forster from over a century ago, about a future that feels uncannily like our present. Called “The Machine Stops,” the story conjures a world of individual humans isolated in such rooms who pass the time by streaming lectures and videoconferencing as the titular Machine tends to their every need. It is a world in which everything — music, food, even your bed — is summoned by the click of a button. In place of work, the Machine offers material and intellectual sustenance. For the story’s main character, Vashti, it turns life into a reassuringly predictable cycle: “[S]he made the room dark and slept; she awoke and made the room light; she ate and exchanged ideas with her friends, and listened to music and attended lectures; she made the room dark and slept. Above her, beneath her, and around her, the Machine hummed eternally.” To Vashti, the Machine offers serenity and certainty in equal measure. In this imagined world of isolated togetherness, heaven is a place. The spiritual godfather of the Beat movement, Mr. Ferlinghetti made his home base in the modest independent book haven now formally known as City Lights Booksellers & Publishers. A self-described “literary meeting place” founded in 1953 and located on the border of the city’s sometimes swank, sometimes seedy North Beach neighborhood, City Lights, on Columbus Avenue, soon became as much a part of the San Francisco scene as the Golden Gate Bridge or Fisherman’s Wharf. (The city’s board of supervisors designated it a historic landmark in 2001.)
The spiritual godfather of the Beat movement, Mr. Ferlinghetti made his home base in the modest independent book haven now formally known as City Lights Booksellers & Publishers. A self-described “literary meeting place” founded in 1953 and located on the border of the city’s sometimes swank, sometimes seedy North Beach neighborhood, City Lights, on Columbus Avenue, soon became as much a part of the San Francisco scene as the Golden Gate Bridge or Fisherman’s Wharf. (The city’s board of supervisors designated it a historic landmark in 2001.) Several years ago, workers breaking ground for a power plant in New Zealand
Several years ago, workers breaking ground for a power plant in New Zealand  The rise of China to the status of economic superpower has been the dominant narrative of the last three decades. China’s rise as the main feature of globalisation, in conjunction with a beneficial sweet spot in demography, drove output up and inflation down in the advanced economies. But these trends are now reversing. China’s economic success depended on many factors, a strong historical social and cultural background, political single-mindedness, a flexible and competent labour force, fed by internal migration, capital controls, developing satisfactory infrastructure and absorption of Western technological know-how. But China’s greatest contribution to global growth is now past. Its working age population is now shrinking, while the ranks of the old expands.
The rise of China to the status of economic superpower has been the dominant narrative of the last three decades. China’s rise as the main feature of globalisation, in conjunction with a beneficial sweet spot in demography, drove output up and inflation down in the advanced economies. But these trends are now reversing. China’s economic success depended on many factors, a strong historical social and cultural background, political single-mindedness, a flexible and competent labour force, fed by internal migration, capital controls, developing satisfactory infrastructure and absorption of Western technological know-how. But China’s greatest contribution to global growth is now past. Its working age population is now shrinking, while the ranks of the old expands. Dreams are full of possibilities; by drifting into the world beyond our waking realities, we can visit magical lands, travel through time and interact with long-lost family and friends. The notion of communicating in real time with someone outside of our dreamscapes, however, sounds like science fiction. A new study demonstrates that, to some extent, this seeming fantasy can be made real. Scientists already knew that one-way contact is attainable. Previous studies have demonstrated that people can process external cues, such as sounds and smells, while asleep. There is also evidence that people are able to send messages in the other direction: Lucid dreamers—those who can become aware they are in a dream—can be trained to signal, using eye movements, that they are in the midst of a dream. Two-way communication, however, is more complex. It requires a person who is asleep to actually understand what they hear from the outside and think about it logically enough to generate an answer, explains Ken Paller, a cognitive neuroscientist at Northwestern University. “We believed that it was going to be possible—but until we actually demonstrated it, we weren’t sure.”
Dreams are full of possibilities; by drifting into the world beyond our waking realities, we can visit magical lands, travel through time and interact with long-lost family and friends. The notion of communicating in real time with someone outside of our dreamscapes, however, sounds like science fiction. A new study demonstrates that, to some extent, this seeming fantasy can be made real. Scientists already knew that one-way contact is attainable. Previous studies have demonstrated that people can process external cues, such as sounds and smells, while asleep. There is also evidence that people are able to send messages in the other direction: Lucid dreamers—those who can become aware they are in a dream—can be trained to signal, using eye movements, that they are in the midst of a dream. Two-way communication, however, is more complex. It requires a person who is asleep to actually understand what they hear from the outside and think about it logically enough to generate an answer, explains Ken Paller, a cognitive neuroscientist at Northwestern University. “We believed that it was going to be possible—but until we actually demonstrated it, we weren’t sure.”