Beasts Bounding Through Time
Van Gogh writing his brother for paints
Hemingway testing his shotgun
Celine going broke as a doctor of medicine
the impossibility of being human
Villon expelled from Paris for being a thief
Faulkner drunk in the gutters of his town
the impossibility of being human
Burroughs killing his wife with a gun
Mailer stabbing his
the impossibility of being human
Maupassant going mad in a rowboat
Dostoyevsky lined up against a wall to be shot
Crane off the back of a boat into the propeller
the impossibility
Sylvia with her head in the oven like a baked potato
Harry Crosby leaping into that Black Sun
Lorca murdered in the road by Spanish troops
the impossibility
Artaud sitting on a madhouse bench
Chatterton drinking rat poison
Shakespeare a plagiarist
Beethoven with a horn stuck into his head against deafness
the impossibility the impossibility
Nietzsche gone totally mad
the impossibility of being human
all too human
this breathing
in and out
out and in
these punks
these cowards
these champions
these mad dogs of glory
moving this little bit of light toward us
impossibly.
by Charles Bukowski
from Poetic Outlaws

 “SOMETIMES I THINK
“SOMETIMES I THINK L
L The crop of Republican candidates running in the midterms has taken immorality to a whole new level. Arizona gubernatorial candidate Kari Lake has
The crop of Republican candidates running in the midterms has taken immorality to a whole new level. Arizona gubernatorial candidate Kari Lake has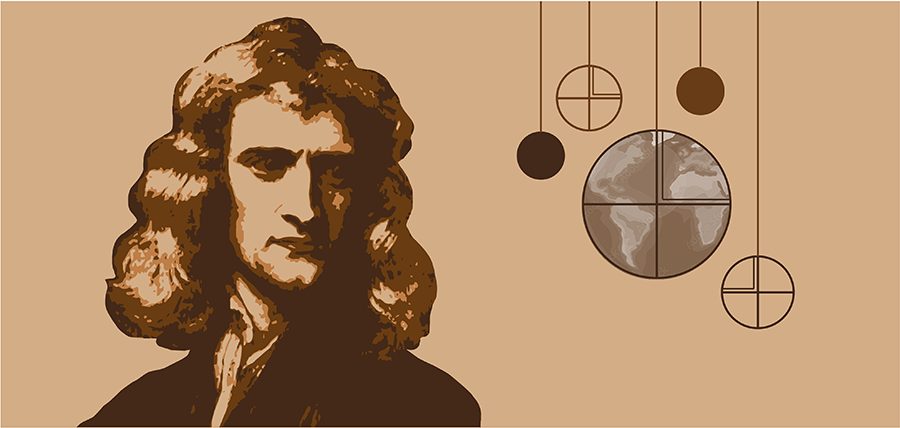 Newton began his quantitative derivation of Earth’s figure in 1686, after learning about work by the French physicist Jean Richer. In 1671, Richer had traveled to Cayenne, the capital of French Guiana in South America, and experimented with a pendulum clock. Richer found that the clock, calibrated to Parisian astronomical time (48°40’ latitude), lost an average of 2.5 minutes per day in Cayenne (5° latitude). This was surprising, but it could be explained by the theory of centrifugal motion, recently developed by Christian Huygens: The theory suggested that the centrifugal effect is strongest at the equator, so the net effective surface gravity would decrease as you moved from Paris to Cayenne[
Newton began his quantitative derivation of Earth’s figure in 1686, after learning about work by the French physicist Jean Richer. In 1671, Richer had traveled to Cayenne, the capital of French Guiana in South America, and experimented with a pendulum clock. Richer found that the clock, calibrated to Parisian astronomical time (48°40’ latitude), lost an average of 2.5 minutes per day in Cayenne (5° latitude). This was surprising, but it could be explained by the theory of centrifugal motion, recently developed by Christian Huygens: The theory suggested that the centrifugal effect is strongest at the equator, so the net effective surface gravity would decrease as you moved from Paris to Cayenne[ From street demonstrations to song, dance, film, and poetry, women are advancing a long legacy of struggle against authoritarianism in Iran.
From street demonstrations to song, dance, film, and poetry, women are advancing a long legacy of struggle against authoritarianism in Iran. Everyone has a type they can’t resist. For the writer Kazuo Ishiguro, it’s old men. Old men secretly worried they’ve spent entire lives on the wrong side of history. Old men born in a world of certainty, transplanted to a different, more dubious one. Old men asking themselves, as so many of us will do (if we haven’t already): ‘What was it all for?’
Everyone has a type they can’t resist. For the writer Kazuo Ishiguro, it’s old men. Old men secretly worried they’ve spent entire lives on the wrong side of history. Old men born in a world of certainty, transplanted to a different, more dubious one. Old men asking themselves, as so many of us will do (if we haven’t already): ‘What was it all for?’ I have a suggestion: Forget London. Forget, for now, the nineteenth century, forget the whole assertion that the value of the “late” or “mature,” Dickens—a construction whose first evidence is usually located by commentators here, in Dombey and Son—rests on his placement of his sentimental melodramas and grotesques in an increasingly deliberate and nuanced social portrait of his times, of his city. Forget institutions, forget reform. Please indulge me, and forget for the moment any questions of psycho-biographical excavation, of self-portraiture, despite Dombey’s being the book which preceded that great dam-bursting of the autobiographical impulse, David Copperfield (and, in fact, Dombey contains a tiny leak in that dam in the form of Mrs. Pipchin, the first character avowed by Dickens to have been drawn from a figure from his life). Forget Where’s Charles Dickens in all this fabulous contradictory stew of story and rhetoric? What does the guy want from us? What does he really think and believe? Forget it all, and then forgive what will surely seem a diminishing suggestion from me, which is that you abandon all context, ye who enter here, and read Dombey and Son as though it were a book about animals.
I have a suggestion: Forget London. Forget, for now, the nineteenth century, forget the whole assertion that the value of the “late” or “mature,” Dickens—a construction whose first evidence is usually located by commentators here, in Dombey and Son—rests on his placement of his sentimental melodramas and grotesques in an increasingly deliberate and nuanced social portrait of his times, of his city. Forget institutions, forget reform. Please indulge me, and forget for the moment any questions of psycho-biographical excavation, of self-portraiture, despite Dombey’s being the book which preceded that great dam-bursting of the autobiographical impulse, David Copperfield (and, in fact, Dombey contains a tiny leak in that dam in the form of Mrs. Pipchin, the first character avowed by Dickens to have been drawn from a figure from his life). Forget Where’s Charles Dickens in all this fabulous contradictory stew of story and rhetoric? What does the guy want from us? What does he really think and believe? Forget it all, and then forgive what will surely seem a diminishing suggestion from me, which is that you abandon all context, ye who enter here, and read Dombey and Son as though it were a book about animals.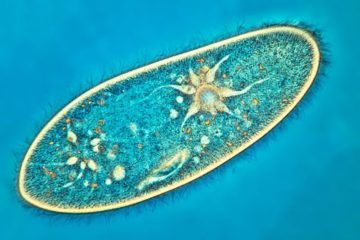 In 1665, the British polymath Robert Hooke published an unexpectedly popular picture book, “Micrographia.” It featured drawings of household objects and inhabitants that were normally barely visible—pests in particular. But they were presented at enormous magnification, having been detected by means of the cutting-edge technology of the day: a compound, two-lens microscope.
In 1665, the British polymath Robert Hooke published an unexpectedly popular picture book, “Micrographia.” It featured drawings of household objects and inhabitants that were normally barely visible—pests in particular. But they were presented at enormous magnification, having been detected by means of the cutting-edge technology of the day: a compound, two-lens microscope.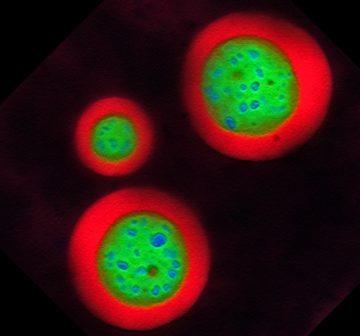 For years, if you asked a scientist how they pictured the inner workings of a cell, they might have spoken of a highly organized factory, with different departments each performing specialized tasks in delineated assembly lines. Ask now, and they might be more inclined to compare the cell to a chaotic open-plan office, with hot-desking zones where different types of cellular matter gather to complete a task and then scatter to other regions.
For years, if you asked a scientist how they pictured the inner workings of a cell, they might have spoken of a highly organized factory, with different departments each performing specialized tasks in delineated assembly lines. Ask now, and they might be more inclined to compare the cell to a chaotic open-plan office, with hot-desking zones where different types of cellular matter gather to complete a task and then scatter to other regions. Rather than repel or frighten him as it might a conventional English gentleman travel-writer, this “atmosphere of entire strangeness” calls to Fermor, pulling him into the fray. Not only does he foray into the local market before even reaching his hotel, but soon afterward he investigates all things Créole—the language, the population, and the dress. Within a mere two days—and despite the fact that Guadeloupe ends up his least inspiring destination—he has so thoroughly immersed himself in the very things whose strangeness had captured his attention that he can bandy Créole patois terms with ease and has decoded the amorous messages indicated by the number of spikes into which the older women tie their silk Madras turbans. What is striking is the thoroughness of his inquiry and his capacity to explain the exotic without eviscerating its alluring quality of otherness.
Rather than repel or frighten him as it might a conventional English gentleman travel-writer, this “atmosphere of entire strangeness” calls to Fermor, pulling him into the fray. Not only does he foray into the local market before even reaching his hotel, but soon afterward he investigates all things Créole—the language, the population, and the dress. Within a mere two days—and despite the fact that Guadeloupe ends up his least inspiring destination—he has so thoroughly immersed himself in the very things whose strangeness had captured his attention that he can bandy Créole patois terms with ease and has decoded the amorous messages indicated by the number of spikes into which the older women tie their silk Madras turbans. What is striking is the thoroughness of his inquiry and his capacity to explain the exotic without eviscerating its alluring quality of otherness. The Criterion Channel is hosting a retrospective of films featuring the late John Garfield, a superstar of the nineteen-forties whose body of work has long gone under-recognized. In the course of a career that stretched from the height of the studio system to the depths of the Red Scare, Garfield pioneered a new, naturalistic approach to acting for the camera, one rooted in the same techniques that would soon be called the
The Criterion Channel is hosting a retrospective of films featuring the late John Garfield, a superstar of the nineteen-forties whose body of work has long gone under-recognized. In the course of a career that stretched from the height of the studio system to the depths of the Red Scare, Garfield pioneered a new, naturalistic approach to acting for the camera, one rooted in the same techniques that would soon be called the  At the dawn of the third millennium, the American novelist Annie Proulx was living in Wyoming and saw a perfect but terrible storm brewing. Extended droughts and warmer winters were providing the optimal conditions for the mountain pine beetle to thrive, and its ongoing infestation—as well as wildfires continuing to ravage the state’s old dense forests, including those of Yellowstone National Park—was turning towering lodgepole pines into ashen tombstones. “That was the first moment when it really sank in that something momentous is going on,” Proulx, who is 87, recently told me over the phone. “I’m a great believer in keeping notes on what you see from year to year. Repetitive observation is my idea of the way to live. This is not a once-in-a-lifetime chance, but a once-in-a-species existence, to observe these huge changes.”
At the dawn of the third millennium, the American novelist Annie Proulx was living in Wyoming and saw a perfect but terrible storm brewing. Extended droughts and warmer winters were providing the optimal conditions for the mountain pine beetle to thrive, and its ongoing infestation—as well as wildfires continuing to ravage the state’s old dense forests, including those of Yellowstone National Park—was turning towering lodgepole pines into ashen tombstones. “That was the first moment when it really sank in that something momentous is going on,” Proulx, who is 87, recently told me over the phone. “I’m a great believer in keeping notes on what you see from year to year. Repetitive observation is my idea of the way to live. This is not a once-in-a-lifetime chance, but a once-in-a-species existence, to observe these huge changes.” Growing between the tides around the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, in the tropical waters of the Indian Ocean, are clusters of what look like tiny, green mushrooms. In fact, this is a type of seaweed, or algae – each one made from a single, gigantic cell.
Growing between the tides around the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, in the tropical waters of the Indian Ocean, are clusters of what look like tiny, green mushrooms. In fact, this is a type of seaweed, or algae – each one made from a single, gigantic cell.