Mariana Lenharo in Nature:
 Science fiction has long entertained the idea of artificial intelligence becoming conscious — think of HAL 9000, the supercomputer-turned-villain in the 1968 film 2001: A Space Odyssey. With the rapid progress of artificial intelligence (AI), that possibility is becoming less and less fantastical, and has even been acknowledged by leaders in AI. Last year, for instance, Ilya Sutskever, chief scientist at OpenAI, the company behind the chatbot ChatGPT, tweeted that some of the most cutting-edge AI networks might be “slightly conscious”.
Science fiction has long entertained the idea of artificial intelligence becoming conscious — think of HAL 9000, the supercomputer-turned-villain in the 1968 film 2001: A Space Odyssey. With the rapid progress of artificial intelligence (AI), that possibility is becoming less and less fantastical, and has even been acknowledged by leaders in AI. Last year, for instance, Ilya Sutskever, chief scientist at OpenAI, the company behind the chatbot ChatGPT, tweeted that some of the most cutting-edge AI networks might be “slightly conscious”.
Many researchers say that AI systems aren’t yet at the point of consciousness, but that the pace of AI evolution has got them pondering: how would we know if they were?
To answer this, a group of 19 neuroscientists, philosophers and computer scientists have come up with a checklist of criteria that, if met, would indicate that a system has a high chance of being conscious.
More here.
 About 10 years ago, a very thick book written by a French economist became a surprising bestseller. It was called
About 10 years ago, a very thick book written by a French economist became a surprising bestseller. It was called  As Borat, the first fake news journalist, I interviewed some college students—three young white men in their ballcaps and polo shirts. It only took a few drinks, and soon they were telling me what they really believed. They asked if, in my country, women are slaves. They talked about how, here in the U.S., “the Jews” have “the upper hand.” When I asked, do you have slaves in America?, they replied, “we wish!” “We should have slaves,” one said, “it would be a better country.” Those young men made a choice. They chose to believe some of the oldest and most vile lies that are at the root of all hate. And so it pains me that we have to say it yet again. The idea that people of color are inferior is a lie. The idea that Jews are dangerous and all-powerful is a lie. The idea that women are not equal to men is a lie. The idea that queer people are a threat to our children is a lie.
As Borat, the first fake news journalist, I interviewed some college students—three young white men in their ballcaps and polo shirts. It only took a few drinks, and soon they were telling me what they really believed. They asked if, in my country, women are slaves. They talked about how, here in the U.S., “the Jews” have “the upper hand.” When I asked, do you have slaves in America?, they replied, “we wish!” “We should have slaves,” one said, “it would be a better country.” Those young men made a choice. They chose to believe some of the oldest and most vile lies that are at the root of all hate. And so it pains me that we have to say it yet again. The idea that people of color are inferior is a lie. The idea that Jews are dangerous and all-powerful is a lie. The idea that women are not equal to men is a lie. The idea that queer people are a threat to our children is a lie. Ten years ago, a tech-savvy group of people with type 1
Ten years ago, a tech-savvy group of people with type 1  ARNOLD SCHOENBERG (1874–1951) was a pivotal figure in the development of 20th-century music. Of the thousands of composers who came before and after him, he stood alone both as the embodiment of the high Romanticism of the 19th and early 20th centuries led by Gustav Mahler, Richard Wagner, and Richard Strauss, and as a rebel who broke down the gates of traditions that had ruled music composition for three centuries. After he spent his childhood in pre–World War I Vienna in a Jewish ghetto, Nazi antisemitism drove him from Europe, eventually to land in Los Angeles, where he stayed to the end of his life, teaching first at USC and then UCLA.
ARNOLD SCHOENBERG (1874–1951) was a pivotal figure in the development of 20th-century music. Of the thousands of composers who came before and after him, he stood alone both as the embodiment of the high Romanticism of the 19th and early 20th centuries led by Gustav Mahler, Richard Wagner, and Richard Strauss, and as a rebel who broke down the gates of traditions that had ruled music composition for three centuries. After he spent his childhood in pre–World War I Vienna in a Jewish ghetto, Nazi antisemitism drove him from Europe, eventually to land in Los Angeles, where he stayed to the end of his life, teaching first at USC and then UCLA.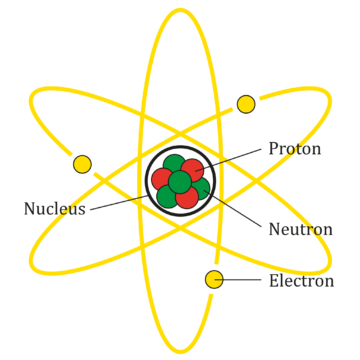 The camera zooms in on the person’s arm to reveal the cells, then a cell nucleus. A DNA strand grows on the screen. The camera focuses on a single atom within the strand, dives into a frenetic cloud of rocketing particles, crosses it, and leaves us in oppressive darkness. An initially imperceptible tiny dot grows smoothly, revealing the atomic nucleus. The narrator lectures that the nucleus of an atom is tens of thousands of times smaller than the atom itself, and poetically concludes that we are made from emptiness.
The camera zooms in on the person’s arm to reveal the cells, then a cell nucleus. A DNA strand grows on the screen. The camera focuses on a single atom within the strand, dives into a frenetic cloud of rocketing particles, crosses it, and leaves us in oppressive darkness. An initially imperceptible tiny dot grows smoothly, revealing the atomic nucleus. The narrator lectures that the nucleus of an atom is tens of thousands of times smaller than the atom itself, and poetically concludes that we are made from emptiness. For more than 50 years, Daniel C. Dennett has been right in the thick of some of humankind’s most meaningful arguments: the nature and function of consciousness and religion, the development and dangers of artificial intelligence and the relationship between science and philosophy, to name a few. For Dennett, an éminence grise of American philosophy who is nonetheless perhaps best known as one of the “four horsemen” of modern atheism alongside Christopher Hitchens, Richard Dawkins and Sam Harris, there are no metaphysical mysteries at the heart of human existence, no magic nor God that makes us who we are. Instead, it’s science and Darwinian evolution all the way down. In his new memoir, “I’ve Been Thinking,” Dennett, a professor emeritus at Tufts University and author of multiple books for popular audiences, traces the development of his worldview, which he is keen to point out is no less full of awe or gratitude than that of those more inclined to the supernatural. “I want people to see what a meaningful, happy life I’ve had with these beliefs,” says Dennett, who is 81. “I don’t need mystery.”
For more than 50 years, Daniel C. Dennett has been right in the thick of some of humankind’s most meaningful arguments: the nature and function of consciousness and religion, the development and dangers of artificial intelligence and the relationship between science and philosophy, to name a few. For Dennett, an éminence grise of American philosophy who is nonetheless perhaps best known as one of the “four horsemen” of modern atheism alongside Christopher Hitchens, Richard Dawkins and Sam Harris, there are no metaphysical mysteries at the heart of human existence, no magic nor God that makes us who we are. Instead, it’s science and Darwinian evolution all the way down. In his new memoir, “I’ve Been Thinking,” Dennett, a professor emeritus at Tufts University and author of multiple books for popular audiences, traces the development of his worldview, which he is keen to point out is no less full of awe or gratitude than that of those more inclined to the supernatural. “I want people to see what a meaningful, happy life I’ve had with these beliefs,” says Dennett, who is 81. “I don’t need mystery.” If you infect a rabbit with a virus or a bacterium, it’ll start to run a fever. Why? The surprising answer is that fever is not a disease; it’s a defence: a useful evolved mechanism that
If you infect a rabbit with a virus or a bacterium, it’ll start to run a fever. Why? The surprising answer is that fever is not a disease; it’s a defence: a useful evolved mechanism that  I have never told this story in its entirety to anyone: not to my therapist, not to my closest friends, and not even to my family. I’ve divulged bits and pieces of it to different people. When my friends back home in Iran asked me why I was leaving, I made up a thousand different reasons. When my friends in Istanbul asked me what happened and why I came, I said that a part of me had died, that my ambition, courage, and hope for the future had dried up. But I didn’t explain why. I couldn’t connect the single moments into a coherent narrative.
I have never told this story in its entirety to anyone: not to my therapist, not to my closest friends, and not even to my family. I’ve divulged bits and pieces of it to different people. When my friends back home in Iran asked me why I was leaving, I made up a thousand different reasons. When my friends in Istanbul asked me what happened and why I came, I said that a part of me had died, that my ambition, courage, and hope for the future had dried up. But I didn’t explain why. I couldn’t connect the single moments into a coherent narrative. WHEN A DEER, A DOE, STEPPED INTO THE ROAD perhaps a hundred and twenty feet ahead of the car I was driving, it seemed for a moment that she would die, even though, during the same moment, I did not feel afraid that I would hit her. I was calm; I returned my smoking hand to the steering wheel; I braked. The deer seemed to be looking at me. There was a chance she might actually run toward me. I switched off the high-beams. All of this happened in two and a half seconds, before the deer continued across the road, safely to the other side, in a single bound. It was then that, exhaling, I realized the extent to which I had felt for—on behalf of—the animal, and for days after I dwelled on the feeling.
WHEN A DEER, A DOE, STEPPED INTO THE ROAD perhaps a hundred and twenty feet ahead of the car I was driving, it seemed for a moment that she would die, even though, during the same moment, I did not feel afraid that I would hit her. I was calm; I returned my smoking hand to the steering wheel; I braked. The deer seemed to be looking at me. There was a chance she might actually run toward me. I switched off the high-beams. All of this happened in two and a half seconds, before the deer continued across the road, safely to the other side, in a single bound. It was then that, exhaling, I realized the extent to which I had felt for—on behalf of—the animal, and for days after I dwelled on the feeling. Drew Gilpin Faust’s memoir is both a moving personal narrative and an enlightening account of the transformative political and social forces that impacted her as she came of age in the 1950s and ’60s. It’s an apt combination from an acclaimed historian who’s also a powerful storyteller.
Drew Gilpin Faust’s memoir is both a moving personal narrative and an enlightening account of the transformative political and social forces that impacted her as she came of age in the 1950s and ’60s. It’s an apt combination from an acclaimed historian who’s also a powerful storyteller. When the diabetes treatments known as GLP-1 analogs reached the market in 2005, doctors advised patients taking the drugs that they might lose a small amount of weight. Talk about an understatement. Obese people can drop more than 15% of their body weight, studies have found, and two of the medications are now approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for weight reduction. A surge in demand for the drugs as slimming treatments has led to shortages. “This class of drugs is exploding in popularity,” says clinical psychologist Joseph Schacht of the University of Colorado School of Medicine.
When the diabetes treatments known as GLP-1 analogs reached the market in 2005, doctors advised patients taking the drugs that they might lose a small amount of weight. Talk about an understatement. Obese people can drop more than 15% of their body weight, studies have found, and two of the medications are now approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for weight reduction. A surge in demand for the drugs as slimming treatments has led to shortages. “This class of drugs is exploding in popularity,” says clinical psychologist Joseph Schacht of the University of Colorado School of Medicine. In 1995, there weren’t many foreign tourists in the country. It was a year after the United States normalized relations with Hanoi and lifted sanctions. Most of the passengers on the flight to Hồ Chí Minh City were Việt kiều, visiting their country for the first time since they left. The tension they felt as they cleared customs was obvious.
In 1995, there weren’t many foreign tourists in the country. It was a year after the United States normalized relations with Hanoi and lifted sanctions. Most of the passengers on the flight to Hồ Chí Minh City were Việt kiều, visiting their country for the first time since they left. The tension they felt as they cleared customs was obvious. In Germany they joke that Slavs live in poverty so they can drive home in a Mercedes. I hadn’t heard this stereotype growing up in so-called Australia. From there, we had to fly.
In Germany they joke that Slavs live in poverty so they can drive home in a Mercedes. I hadn’t heard this stereotype growing up in so-called Australia. From there, we had to fly.