Henry Farrell in American Affairs:
It’s a rare buccaneer who runs a book club. But in October 2012, the chief administrator of the Silk Road drug market, under the pseudonym “Dread Pirate Roberts,” was on the dark web assigning readings from the anarchist libertarian philosophy of Murray Rothbard. Rothbard had argued that markets and individual connections were really all we needed. As the Dread Pirate, whose real name was Ross Ulbricht, summarized it, a happier world awaited those who took the exit road from ordinary politics. They could escape the “thieving murderous mits [sic]” of the state to embrace the freedom that emerged from a “multitude of voluntary interactions between individuals.”
For Ulbricht, Silk Road wasn’t just a way to make money but the tech-fueled expression of a political philosophy. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin had (supposedly) enabled a new realm of voluntary exchange outside the grasp of government, allowing people to buy and sell drugs and guns without the feds interfering. Of course, state tyranny might reemerge if voluntary organizations like Silk Road started to steal from their users, or spied on, or even killed them. Ulbricht, however, believed that the forces of market competition would prevent this from happening, leading to “freedom and prosperity the likes of which the world has never known.”
Ambitious libertarian projects to escape the sordid compromises of politics have been part of Silicon Valley culture since the beginning. But Ulbricht’s dream of escape from politics and its vexations has become increasingly influential in the decade since the Dread Pirate Roberts book club. Several prominent Silicon Valley investors and entrepreneurs have become disenchanted with the U.S. government, East Coast media, and even their own employees (which have all increasingly become disenchanted with them).
More here.
Enjoying the content on 3QD? Help keep us going by donating now.

 A
A “Mr. Handel’s head is more full of Maggots than ever. … I could tell you more … but it grows late & I must defer the rest until I write next; by which time, I doubt not, more new ones will breed in his Brain.”
“Mr. Handel’s head is more full of Maggots than ever. … I could tell you more … but it grows late & I must defer the rest until I write next; by which time, I doubt not, more new ones will breed in his Brain.” There were, of course, other ways to feel connected with humanity on a plane. You could notice a slight indentation left in the seat from the person before you, or the length to which they had extended (or shortened) their seatbelt, which would now become yours. You didn’t have to turn to the back of the in-flight magazine to see some stranger’s—or, more likely, strangers’—handiwork on the crossword, or wonder what flavor of sticky substance someone had spilled across its pages. Nor was it required to retrace the doodles drawn on the ads for UNTUCKit shirts, It’s Just Lunch, Hard Rock Café, Wellendorff jewelry, companies selling gold coins, and Big Green Eggs. But it’s clear that with the last print issue of Hemispheres, the in-flight magazine of United Airlines, and the last such magazine connected to a major US carrier (with the exception of Hana Hou!, for Hawaiian Airlines), it is the end of an era.
There were, of course, other ways to feel connected with humanity on a plane. You could notice a slight indentation left in the seat from the person before you, or the length to which they had extended (or shortened) their seatbelt, which would now become yours. You didn’t have to turn to the back of the in-flight magazine to see some stranger’s—or, more likely, strangers’—handiwork on the crossword, or wonder what flavor of sticky substance someone had spilled across its pages. Nor was it required to retrace the doodles drawn on the ads for UNTUCKit shirts, It’s Just Lunch, Hard Rock Café, Wellendorff jewelry, companies selling gold coins, and Big Green Eggs. But it’s clear that with the last print issue of Hemispheres, the in-flight magazine of United Airlines, and the last such magazine connected to a major US carrier (with the exception of Hana Hou!, for Hawaiian Airlines), it is the end of an era.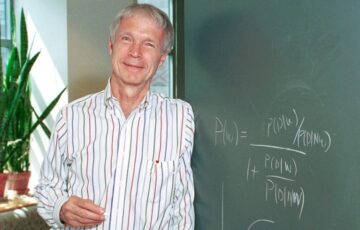 John Hopfield, one of this year’s
John Hopfield, one of this year’s  The publication of new interviews with Donald Trump’s longstanding chief of staff John Kelly have been in the news since last week, and the Harris campaign has picked up on Kelly’s use of the word “fascist” to describe his former boss. This has reignited a longstanding debate over whether Trump and his MAGA movement represent the threat of genuine fascism in the United States were he to be re-elected.
The publication of new interviews with Donald Trump’s longstanding chief of staff John Kelly have been in the news since last week, and the Harris campaign has picked up on Kelly’s use of the word “fascist” to describe his former boss. This has reignited a longstanding debate over whether Trump and his MAGA movement represent the threat of genuine fascism in the United States were he to be re-elected. In the brief introduction to
In the brief introduction to  Capitalism thwarts and stunts the creativity of human beings. It robs the mass of the population of control over their own labour, and therefore over production generally. It denies the vast majority of people creative expression in their daily work lives, and this affects all of life. Workers are robbed not just of artistic creativity but even of our potential to be an audience for art. Yet there is a constant struggle to free humanity’s potential. And there have always been troublesome artists and troublesome art. The contradictions of capitalism mean that it is possible, at least to some extent, for artistic expression to develop in opposition to the dominant trajectory of society. Bertolt Brecht’s poem “Motto” makes the point:
Capitalism thwarts and stunts the creativity of human beings. It robs the mass of the population of control over their own labour, and therefore over production generally. It denies the vast majority of people creative expression in their daily work lives, and this affects all of life. Workers are robbed not just of artistic creativity but even of our potential to be an audience for art. Yet there is a constant struggle to free humanity’s potential. And there have always been troublesome artists and troublesome art. The contradictions of capitalism mean that it is possible, at least to some extent, for artistic expression to develop in opposition to the dominant trajectory of society. Bertolt Brecht’s poem “Motto” makes the point: L
L New image-making technologies
New image-making technologies