Shelly Fan in Singularity Hub:
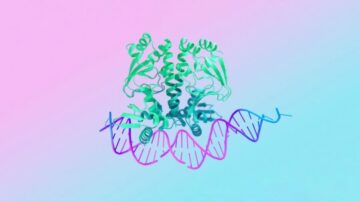 Proteins are biological workhorses. They build our bodies and orchestrate the molecular processes in cells that keep them healthy. They also present a wealth of targets for new medications. From everyday pain relievers to sophisticated cancer immunotherapies, most current drugs interact with a protein. Deciphering protein architectures could lead to new treatments. That was the promise of AlphaFold 2, an AI model from Google DeepMind that predicted how proteins gain their distinctive shapes based on the sequences of their constituent molecules alone. Released in 2020, the tool was a breakthrough half a decade in the making. But proteins don’t work alone. They inhabit an entire cellular universe and often collaborate with other molecular inhabitants like, for example, DNA, the body’s genetic blueprint.
Proteins are biological workhorses. They build our bodies and orchestrate the molecular processes in cells that keep them healthy. They also present a wealth of targets for new medications. From everyday pain relievers to sophisticated cancer immunotherapies, most current drugs interact with a protein. Deciphering protein architectures could lead to new treatments. That was the promise of AlphaFold 2, an AI model from Google DeepMind that predicted how proteins gain their distinctive shapes based on the sequences of their constituent molecules alone. Released in 2020, the tool was a breakthrough half a decade in the making. But proteins don’t work alone. They inhabit an entire cellular universe and often collaborate with other molecular inhabitants like, for example, DNA, the body’s genetic blueprint.
This week, DeepMind and Isomorphic Labs released a big new update that allows the algorithm to predict how proteins work inside cells. Instead of only modeling their structures, the new version—dubbed AlphaFold 3—can also map a protein’s interactions with other molecules. For example, could a protein bind to a disease-causing gene and shut it down? Can adding new genes to crops make them resilient to viruses? Can the algorithm help us rapidly engineer new vaccines to tackle existing diseases—or whatever new ones nature throws at us? “Biology is a dynamic system…you have to understand how properties of biology emerge due to the interactions between different molecules in the cell,” said Demis Hassabis, the CEO of DeepMind, in a press conference. AlphaFold 3 helps explain “not only how proteins talk to themselves, but also how they talk to other parts of the body,” said lead author Dr. John Jumper.
More here.
