Sara Reardon in Science:
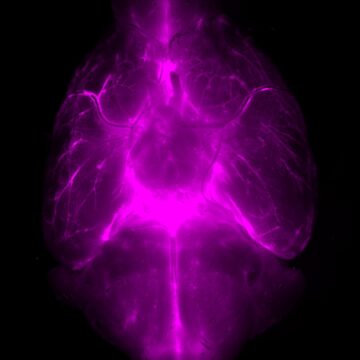 We all need sleep, but no one really knows why. For the past 10 years, a prevailing theory has been that a key function of sleep is to wash waste products and toxins from the brain via a series of tiny channels called the glymphatic system. Sleep problems can disrupt this process, the theory’s proponents say, perhaps raising the risk of Alzheimer’s disease and other brain disorders. Mouse experiments seem to support the idea. But in recent years, several groups of scientists have challenged some aspects of the theory. Now, a new study has found that the mouse brain clears small dye molecules more efficiently while the animal is awake than when it is asleep or under anesthesia. A glymphatic system might still cleanse the brain, the researchers say, but sleep actually slows this cleansing down.
We all need sleep, but no one really knows why. For the past 10 years, a prevailing theory has been that a key function of sleep is to wash waste products and toxins from the brain via a series of tiny channels called the glymphatic system. Sleep problems can disrupt this process, the theory’s proponents say, perhaps raising the risk of Alzheimer’s disease and other brain disorders. Mouse experiments seem to support the idea. But in recent years, several groups of scientists have challenged some aspects of the theory. Now, a new study has found that the mouse brain clears small dye molecules more efficiently while the animal is awake than when it is asleep or under anesthesia. A glymphatic system might still cleanse the brain, the researchers say, but sleep actually slows this cleansing down.
Other researchers are stumped as to how to explain the opposing results, and several declined to comment on the record for fear of entering a heated debate. A few see the new findings as a serious blow to the sleep clearance theory, but others say the new paper’s methods are too different from those of the earlier work to credibly challenge it. “When you criticize a concept that has been there for some time, then your design should be even better,” says Per Kristian Eide of the University of Oslo.
More here.
