From CDC Newsroom:
 This year’s report showed that overall cancer death rates decreased 1.5% on average per year from 2001 to 2017, decreasing more rapidly among men (by 1.8% per year) than among women (1.4% per year). The report found that overall cancer death rates decreased in every racial and ethnic group during 2013–2017. “The United States continues to make significant progress in cancer prevention, early detection, and treatment,” said CDC Director Robert R. Redfield, M.D. “While we are encouraged that overall cancer death rates have decreased, there is still much more we can do to prevent new cancers and support communities, families, and cancer survivors in this ongoing battle.”
This year’s report showed that overall cancer death rates decreased 1.5% on average per year from 2001 to 2017, decreasing more rapidly among men (by 1.8% per year) than among women (1.4% per year). The report found that overall cancer death rates decreased in every racial and ethnic group during 2013–2017. “The United States continues to make significant progress in cancer prevention, early detection, and treatment,” said CDC Director Robert R. Redfield, M.D. “While we are encouraged that overall cancer death rates have decreased, there is still much more we can do to prevent new cancers and support communities, families, and cancer survivors in this ongoing battle.”
National Status of Cancer Report Findings
The data analyzed in the report combines cancer incidence data collected by CDC’s National Program of Cancer Registries (NPCR) and NCI’s Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program, as well as mortality data from CDC’s National Center for Health Statistics.
The report found that from 2013 to 2017:
Among men, death rates decreased for 11 of the 19 most common cancers, were stable for four cancers (including prostate), and increased for four cancers (oral cavity and pharynx, soft tissue including heart, brain and other nervous system, and pancreas). Among women, death rates decreased for 14 of the 20 most common cancers, including the three most common cancers (lung and bronchus, breast, and colorectal), but increased for cancers of the uterus, liver, brain and other nervous system, soft tissue including heart, and pancreas. Rates were stable for oral cavity and pharynx cancer. Overall cancer death rates among children ages 0 to 14 years decreased an average of 1.4% per year. Among adolescents and young adults ages 15 to 39 years, overall cancer death rates decreased an average of 1.0% per year. Melanoma death rates decreased 6.1% per year among men and 6.3% per year among women. Lung cancer death rates decreased 4.8% per year among men and 3.7% per year among women. However, lung cancer continues to be the leading cause of cancer death, accounting for about one-fourth of all cancer deaths.
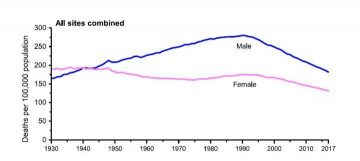
More here. (Note: Mortality from cancer increased for 60 years in parallel with increase in smoking, and now has declined steadily by 1% a year mostly because of effective anti-smoking campaigns bringing the death rate down to what it was in 1930)
