by Lexi Lerner
Traveling to a place where no one knows you, nor where anyone’s particularly interested, is terrestrially analogous to Carl Sagan’s Pale Blue Dot. So far away from home, you look over your shoulder at that bright, dense pinprick of everything you’ve ever understood, valued, loved, identified as… and think to yourself: That means nothing out here.

Of course there is the celebrated, luxurious trope of “finding yourself” through travel. But after staring for a long while at the Pale Blue Dot, a disconcerting tannin lingers: a smallness, an inconsequentiality, that renders you and that dense dot mutually invisible, mutually unintelligible. While everything in the universe gravitationally pulls at each other – Voyager 1 to the Dot, me to you – distance makes that attraction faint to the point of unaccountability, or (the semblance of) estrangement. A homelessness that cannot be shaken once felt, even after some sort of return or reconciliation. It’s not finding, it’s losing – irrecoverably.
If all the contextual factors that justified my personhood, that explained the aggregate of my experiences, carved a river of my self, moving to Vienna caused that river to pool out into senseless water: atomized, oceanic, dilute… it could no longer be called a river, or anything at all, really. No house of language could domesticate this gargantuan puddle.
And perhaps there was no river from the start – just a canal calling itself destined so it could keep flowing when it needed to.
First week field notes:
- In summertime the Viennese expel themselves into the countryside like fry from a seahorse. The city is left flabby, its stretch marks the too-wide streets and the too-wide sidewalks. In fact, two sidewalks often run parallel to each other on the same side of the road, accompanied by a stately line of maples, plus an extra bike lane or two, then six lanes of traffic, and the same pedestrian palace road mirrored on the other side. Anticipating throngs that never come.
- There is a preoccupation with modern interior design: mod shapes in natural fibers like wool and wood and cotton and bamboo, the furniture interesting as art pieces but wholly unwelcoming to engage with. In every living room hangs the same Ikea light fixture that looks like a dandelion made of spikes. The chairs purse their lips as you sit. Most don’t have arms.
- Vienna has shoe culture (no trekking dirt into any room past the foyer.) Yet the Viennese don’t walk quietly. Boots clomp on hardwood, on cobblestone. But the architecture is so gaping that it leaves enormous space for silence. That silence fills space.
- The same wind roars through the Augarten tree corridors and the Untergrundbahn tunnels. It’s a kind of wind that sneaks up on you, where you only hear it and see it as you feel it.
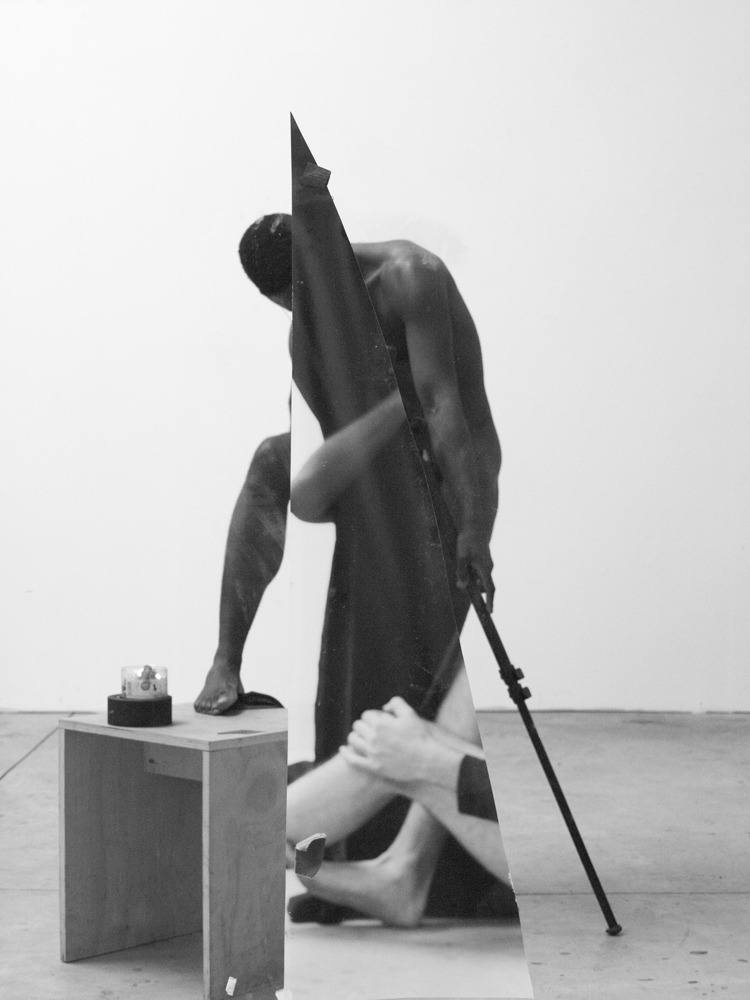



 In the science fiction short story “
In the science fiction short story “
 The major “National-Socialist Underground” trial
The major “National-Socialist Underground” trial  The ill-defined term ‘populism’ is used in different senses not just by common people or the media, but even among social scientists. Economists usually interpret it as short-termism at the expense of the long-term health of the economy. They usually refer to it in describing macro-economic profligacy, leading to galloping budget deficits in pandering to all kinds of pressure groups for larger government spending and to the consequent inflation—examples abound in the recent history of Latin America (currently in virulent display in Venezuela). Political scientists, on the other hand, refer to the term in the context of a certain widespread distrust in the institutions of representative democracy, when people look for a strong leader who can directly embody the ‘popular will’ and cut through the tardy processes of the rule of law and encumbrances like basic human rights or minority rights. Even though I am an economist, in this article I shall mainly confine myself to the latter use of the term.
The ill-defined term ‘populism’ is used in different senses not just by common people or the media, but even among social scientists. Economists usually interpret it as short-termism at the expense of the long-term health of the economy. They usually refer to it in describing macro-economic profligacy, leading to galloping budget deficits in pandering to all kinds of pressure groups for larger government spending and to the consequent inflation—examples abound in the recent history of Latin America (currently in virulent display in Venezuela). Political scientists, on the other hand, refer to the term in the context of a certain widespread distrust in the institutions of representative democracy, when people look for a strong leader who can directly embody the ‘popular will’ and cut through the tardy processes of the rule of law and encumbrances like basic human rights or minority rights. Even though I am an economist, in this article I shall mainly confine myself to the latter use of the term. When Mrs. William Shakespeare died on this August day in 1623, her family and friends believed they would lay her to eternal rest beside her renowned husband. They did not. They did inter an ordinary wife and mother, but the memory of her went out to become a Frankenstein monster, cut up and reassembled down the centuries. Few of the many makeovers done to Anne Hathaway Shakespeare since her passing have been flattering.
When Mrs. William Shakespeare died on this August day in 1623, her family and friends believed they would lay her to eternal rest beside her renowned husband. They did not. They did inter an ordinary wife and mother, but the memory of her went out to become a Frankenstein monster, cut up and reassembled down the centuries. Few of the many makeovers done to Anne Hathaway Shakespeare since her passing have been flattering.
 I’m tempted to describe Marion Milner’s book A Life of One’s Own as the missing manual for owners of a human mind. However, it’s not didactic or prescriptive. In fact, it’s useful mainly because it’s nothing like a manual or a self-help book. The book is more like an insightful travelogue by an articulate and honest observer with a gift for using vivid physical imagery and metaphors to describe her inner world.
I’m tempted to describe Marion Milner’s book A Life of One’s Own as the missing manual for owners of a human mind. However, it’s not didactic or prescriptive. In fact, it’s useful mainly because it’s nothing like a manual or a self-help book. The book is more like an insightful travelogue by an articulate and honest observer with a gift for using vivid physical imagery and metaphors to describe her inner world.
 The 2020s will have a name. In the nursing homes of the future, Millennials’ grandchildren will hear all about the coming decade. Gran will remove her headset, loaded out with VR-entertainment and the latest in biometric tech, and she’ll tell the kids about the world as it was in the third decade of the 21st Century. For now, we look ahead to the Twenties, a decade certain to be charged with meaning, roaring in one way or another.
The 2020s will have a name. In the nursing homes of the future, Millennials’ grandchildren will hear all about the coming decade. Gran will remove her headset, loaded out with VR-entertainment and the latest in biometric tech, and she’ll tell the kids about the world as it was in the third decade of the 21st Century. For now, we look ahead to the Twenties, a decade certain to be charged with meaning, roaring in one way or another. One of my favorite quotes about artificial intelligence is often attributed to pioneering computer scientists Hans Moravec and Marvin Minsky. To paraphrase: “The most important thing we have learned from three decades of AI research is that the hard things are easy and the easy things are hard”. In other words, we have been hoodwinked for a long time. We thought that vision and locomotion and housework would be easy and language recognition and chess and driving would be hard. And yet it has turned out that we have made significant strides in tackling the latter while hardly making a dent in the former. The lower-level skills seem to require significantly more understanding and computational power than seemingly more sophisticated, higher-level skills.
One of my favorite quotes about artificial intelligence is often attributed to pioneering computer scientists Hans Moravec and Marvin Minsky. To paraphrase: “The most important thing we have learned from three decades of AI research is that the hard things are easy and the easy things are hard”. In other words, we have been hoodwinked for a long time. We thought that vision and locomotion and housework would be easy and language recognition and chess and driving would be hard. And yet it has turned out that we have made significant strides in tackling the latter while hardly making a dent in the former. The lower-level skills seem to require significantly more understanding and computational power than seemingly more sophisticated, higher-level skills.

