Ewen Callaway in Nature:
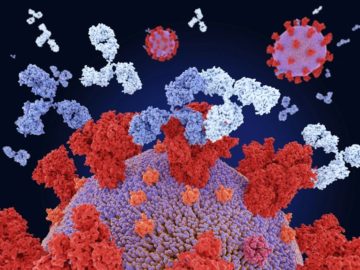 At the height of the pandemic, researchers raced to develop some of the first effective treatments against COVID-19: antibody molecules isolated from the blood of people who had recovered from the disease.
At the height of the pandemic, researchers raced to develop some of the first effective treatments against COVID-19: antibody molecules isolated from the blood of people who had recovered from the disease.
Now, scientists have shown that generative artificial intelligence (AI) can provide a shortcut through some of this laborious process, suggesting sequences that boost the potency of antibodies against viruses such as SARS-CoV-2 and ebolavirus. A study published last week in Nature Biotechnology1 is part of growing efforts to apply ‘neural networks’ similar to those behind the ChatGPT AI platform to antibody design.
More here.
