Helen Thomson in New Scientist:
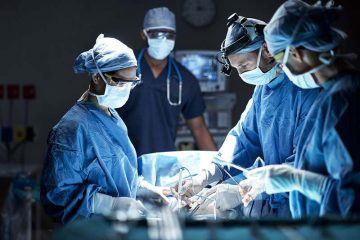 The technique, officially called emergency preservation and resuscitation (EPR), is being carried out on people who arrive at the University of Maryland Medical Centre in Baltimore with an acute trauma – such as a gunshot or stab wound – and have had a cardiac arrest. Their heart will have stopped beating and they will have lost more than half their blood. There are only minutes to operate, with a less than 5 per cent chance that they would normally survive.
The technique, officially called emergency preservation and resuscitation (EPR), is being carried out on people who arrive at the University of Maryland Medical Centre in Baltimore with an acute trauma – such as a gunshot or stab wound – and have had a cardiac arrest. Their heart will have stopped beating and they will have lost more than half their blood. There are only minutes to operate, with a less than 5 per cent chance that they would normally survive.
EPR involves rapidly cooling a person to around 10 to 15°C by replacing all of their blood with ice-cold saline. The patient’s brain activity almost completely stops. They are then disconnected from the cooling system and their body – which would otherwise be classified as dead – is moved to the operating theatre.
A surgical team then has 2 hours to fix the person’s injuries before they are warmed up and their heart restarted.
More here.
