Adrienne LaFrance in The Atlantic:
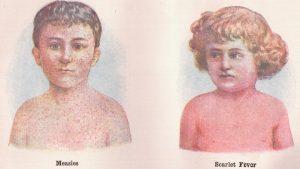 Before vaccination became widespread in the 1960s, pediatricians knew to check their patients’ throats for the spray of telltale spots. Scientists raced for decades to develop an effective vaccine. And in the meantime, newspapers printed matter-of-fact death tolls, tallying high numbers of deaths by measles, scarlet fever, smallpox, and other illnesses of the recent past.
Before vaccination became widespread in the 1960s, pediatricians knew to check their patients’ throats for the spray of telltale spots. Scientists raced for decades to develop an effective vaccine. And in the meantime, newspapers printed matter-of-fact death tolls, tallying high numbers of deaths by measles, scarlet fever, smallpox, and other illnesses of the recent past.
People expected to get measles in those days, but they didn’t expect to survive. Measles killed some 2.6 million people each year before vaccination was widespread, according to the World Health Organization. Today, some 145,000 people die of measles each year—most of them because they lack access to the vaccine—and just a tiny fraction of them are in the United States, where the vaccine is readily available and widely used.
Traces of measles’ one-time ubiquity in the States still linger in morbid nursery rhymes (“Cat’s got the measles and the measles have got you,” one goes) and splotchy illustrations in old children’s books and medical texts, but vaccination has changed the way people see the illness in the developed world.
More here.
