by Eric J. Weiner
Ghazal: India’s Season of Dissent by Karthika Naïr[1]

This year, this night, this hour, rise to salute the season of dissent.
Sikhs, Hindus, Muslims—Indians, all—seek their nation of dissent.
We the people of…they chant: the mantra that birthed a republic.
Even my distant eyes echo flares from this beacon of dissent.
Kolkata, Kasargod, Kanpur, Nagpur, Tripura… watch it spread,
tip to tricoloured tip, then soar: the winged horizon of dissent.
Dibrugarh: five hundred students face the CAA and lathiwielding
cops with Tagore’s song—an age-old tradition of dissent.
Kaagaz nahin dikhayenge… Sab Kuch Yaad Rakha Jayega…
Poetry, once more, stands tall, the Grand Central Station of dissent.
Aamir Aziz, Kausar Munir, Varun Grover, Bisaralli…
Your words, in many tongues, score the sky: first citizens of dissent.
We shall see/ Surely, we too shall see. Faiz-saab, we see your greatness
scanned for “anti-Hindu sentiment”, for the treason of dissent.
Delhi, North-East: death flanks the anthem of a once-secular land
where police now maim Muslims with Sing and die, poison of dissent.
A government of the people, by the people, for the people,
has let slip the dogs of carnage for swift excision of dissent.
Name her, Ka, name her. Umme Habeeba, mere-weeks-old, braves frost and
fascism from Shaheen Bagh: our oldest, finest reason for dissent.
As democracies wither and die throughout the world, Karthika Naïr’s ghazal is a passionate and timely celebration of dissent. The places, peoples, and languages of India dance, crack, bleed, demand, and sing their dissent. Soaring through and beyond the borders of India’s post-colonial history, dissent is the oxygen of freedom, scoring the sky with “words, in many tongues.” The “winged horizon of dissent” delineates “what is” from what should be; it is a practice of the radical imagination, an articulation of audacious hope in the long shadows of broken promises and paralyzing fatalism. As the malcontent’s muse, dissent drives the radical desires of dissident artists and intellectuals, the pedagogues of utopic possibilities at a time in which, as Naïr pointedly says,
…there are no small freedoms…I think that India is unfortunately right now living proof for anybody who wants to see the chronicle of an ascension of totalitarianism. This is the chronology: the loss of greater freedoms comes in the slipstream of the denial of perceived “smaller” freedoms. It’s an incremental approach. First, almost always, they come for the books, the art, the movies, the seemingly frivolous things. I would trace it all the way back to the first book banned in independent India, whatever the reason. Because if you can police the imagination, control the freedom of the mind, then everything else will fall in line. There can never be adequate protection for, or vigilance over, these.
Naïr’s poem is also a warning that without dissenting voices, bodies, and minds the promises—explicit and implied—of democracy, like the bones of a malnourished child, will break. Its demise is barely audible against the pitch of rage spewing from the mouths of autocrats and their sycophants throughout the world. These “dogs of carnage” are unleashed, roaming urban streets and dusty squares, rabidly tearing the flesh of hope from the bones of people who have the audacity to dissent. Read more »
 Researchers at the DZNE and the University Medical Center Göttingen (UMG) have identified molecules in the blood that can indicate impending dementia. Their findings, which are presented in the scientific journal EMBO Molecular Medicine, are based on human studies and laboratory experiments. University hospitals across Germany were also involved in the investigations. The biomarker described by the team led by Prof. André Fischer is based on measuring levels of so-called microRNAs. The technique is not yet suitable for practical use; the scientists therefore aim to develop a simple blood test that can be applied in routine medical care to assess dementia risk. According to the study data, microRNAs could potentially also be targets for dementia therapy.
Researchers at the DZNE and the University Medical Center Göttingen (UMG) have identified molecules in the blood that can indicate impending dementia. Their findings, which are presented in the scientific journal EMBO Molecular Medicine, are based on human studies and laboratory experiments. University hospitals across Germany were also involved in the investigations. The biomarker described by the team led by Prof. André Fischer is based on measuring levels of so-called microRNAs. The technique is not yet suitable for practical use; the scientists therefore aim to develop a simple blood test that can be applied in routine medical care to assess dementia risk. According to the study data, microRNAs could potentially also be targets for dementia therapy.
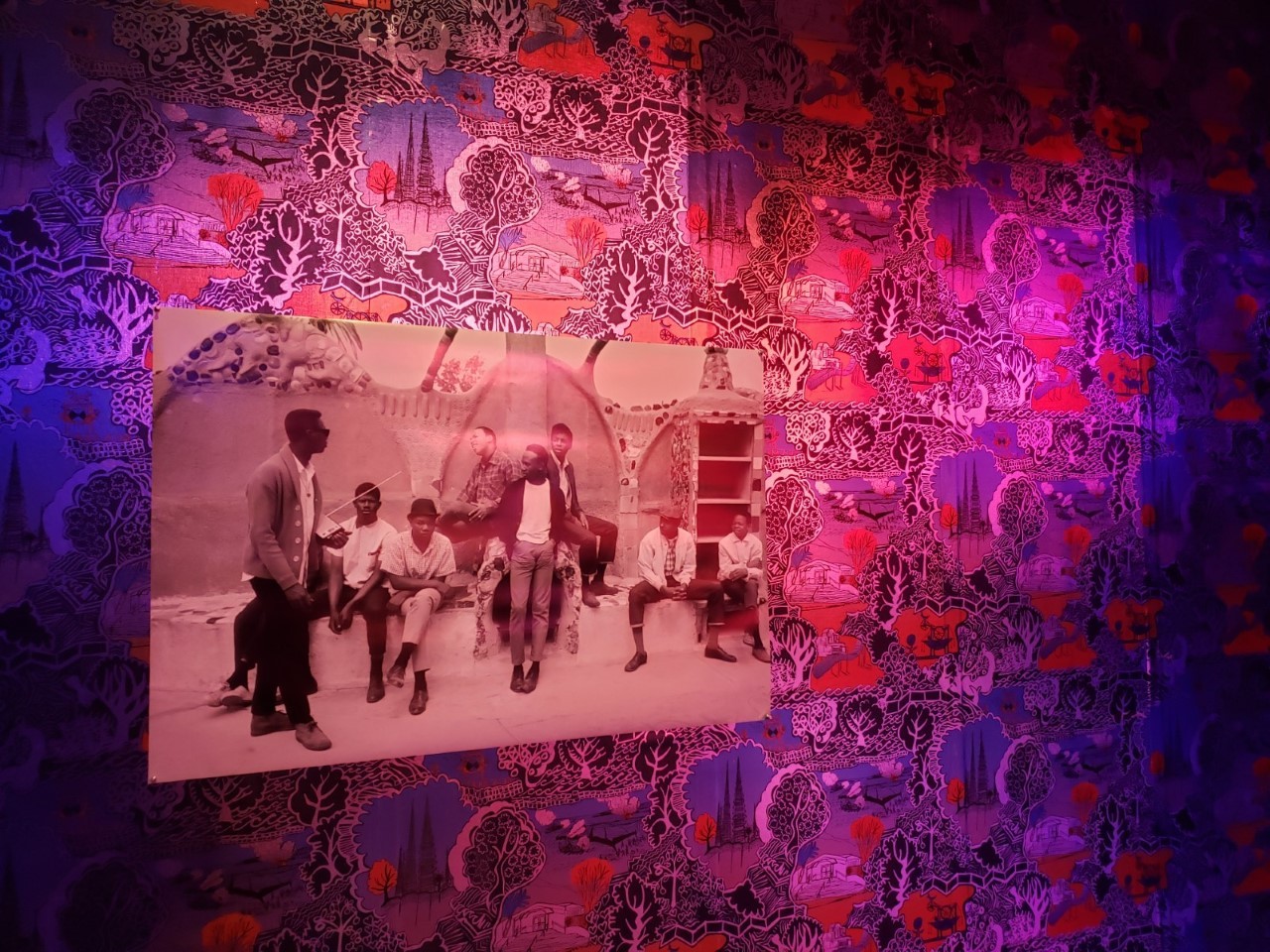
 Cauleen Smith. Space Station Chinoiserie #1: Take hold of the Clouds, 2018.
Cauleen Smith. Space Station Chinoiserie #1: Take hold of the Clouds, 2018. Last night I (Danielle Spencer) went to the New York Film Festival screening of Memoria (dir. Apichatpong Weerasethakul) in Alice Tully hall at Lincoln Center. I last joined a large gathering 19 months ago, in March of 2020.
Last night I (Danielle Spencer) went to the New York Film Festival screening of Memoria (dir. Apichatpong Weerasethakul) in Alice Tully hall at Lincoln Center. I last joined a large gathering 19 months ago, in March of 2020.
 In the world of Star Trek, no one ever goes hungry or lacks access to healthcare. No one wants for housing, education, social inclusion or any other basic need. In fact, no citizen of the United Federation of Planets is ever seen to pay for everyday goods or services, only for gambling or special entertainments. The Federation suffers no scarcity of any kind. All waste is presumably fed into the replicators and turned into fresh food or new clothes or whatever is needed. Yet despite ample social safety nets, there’s no end to internecine politicking, human foibles and failures, corruption and vanity, charisma and venality. The world of Star Trek appeals so widely, I think, because it presents us with something colorfully short of a utopia, a flawed human attempt toward a just, caring, and individually enabling social order. It imagines a society based on a shared set of human values—fairness, cooperation, political and economic egalitarianism—where basic human needs are equitably answered so that no one has to compete for basic subsistence and wellbeing. As the venerable
In the world of Star Trek, no one ever goes hungry or lacks access to healthcare. No one wants for housing, education, social inclusion or any other basic need. In fact, no citizen of the United Federation of Planets is ever seen to pay for everyday goods or services, only for gambling or special entertainments. The Federation suffers no scarcity of any kind. All waste is presumably fed into the replicators and turned into fresh food or new clothes or whatever is needed. Yet despite ample social safety nets, there’s no end to internecine politicking, human foibles and failures, corruption and vanity, charisma and venality. The world of Star Trek appeals so widely, I think, because it presents us with something colorfully short of a utopia, a flawed human attempt toward a just, caring, and individually enabling social order. It imagines a society based on a shared set of human values—fairness, cooperation, political and economic egalitarianism—where basic human needs are equitably answered so that no one has to compete for basic subsistence and wellbeing. As the venerable 

 What is the present? When did it begin? Stoics simply consult the calendar for an answer, where they find each new span of 24 hours reassuringly dubbed Today. Archaeologists speak of “Years Before Present” when referring to the time prior to January 1, 1950, the arbitrarily chosen inauguration of the era of radiocarbon dating following the explosion of the first atomic bombs. And the Judeo-Christian West makes of the present age a spatio-temporal chronotope, a narrative rooted in the time and place of birth of a particular figure, whose “presence” as guarantor is inextricable from the dating system, whether the appellations used are the frankly messianic Before Christ and Anno Domini, or the compromise variations on an ecumenical “Common Era”.
What is the present? When did it begin? Stoics simply consult the calendar for an answer, where they find each new span of 24 hours reassuringly dubbed Today. Archaeologists speak of “Years Before Present” when referring to the time prior to January 1, 1950, the arbitrarily chosen inauguration of the era of radiocarbon dating following the explosion of the first atomic bombs. And the Judeo-Christian West makes of the present age a spatio-temporal chronotope, a narrative rooted in the time and place of birth of a particular figure, whose “presence” as guarantor is inextricable from the dating system, whether the appellations used are the frankly messianic Before Christ and Anno Domini, or the compromise variations on an ecumenical “Common Era”.



 I recently spent a few weeks in the UK, which is suffering from a labor shortage post lockdown like the US. Though, unlike the US, some of the UK’s problems are self-inflicted Brexit wounds. The shortages are rippling through every sector, and as in the US, that includes hospitality. Coming out of lockdown, no doubt initiated by hygiene concerns, some restaurants I visited in New York used QR codes instead of handing out menus.
I recently spent a few weeks in the UK, which is suffering from a labor shortage post lockdown like the US. Though, unlike the US, some of the UK’s problems are self-inflicted Brexit wounds. The shortages are rippling through every sector, and as in the US, that includes hospitality. Coming out of lockdown, no doubt initiated by hygiene concerns, some restaurants I visited in New York used QR codes instead of handing out menus.  Shortly after my arrival at Cambridge I struck up a warm friendship with a very bright young faculty member, Jim Mirrlees (who was to get the Nobel Prize later), recently returned from a stint of research in India. (Although he was a high-powered theoretical economist, he had what seemed to me an almost religious/moral fervor for doing something to help poor countries). Even more than Frank Hahn, he got involved in the theoretical analysis in my dissertation, and helped me in making some of the proofs of my propositions simpler and less inelegant.
Shortly after my arrival at Cambridge I struck up a warm friendship with a very bright young faculty member, Jim Mirrlees (who was to get the Nobel Prize later), recently returned from a stint of research in India. (Although he was a high-powered theoretical economist, he had what seemed to me an almost religious/moral fervor for doing something to help poor countries). Even more than Frank Hahn, he got involved in the theoretical analysis in my dissertation, and helped me in making some of the proofs of my propositions simpler and less inelegant. What is weather? Its etymology is not, as one may have hoped, connected to “whether”, as in “that which may be either one way, or the other” —“Whether the picnic is on or not depends on whether it rains”—, though both words have equally fascinating Germanic pedigrees. The modern German Wetter originally described the sort of ferocious wind you might encounter at a mountain peak, and later took on the primary connotation of “bad weather”, or, as is said in German, Unwetter, where the prefix that ordinarily signifies negation or absence, Un-, comes instead to indicate intensification (as in Untier — seemingly “non-animal” but literally “monster”, or Unkraut — seemingly “non-herb” but literally “weed”). At the outset then we may say that weather, strangely, is something the negative instances of which are also its paradigm instances. Yet the German and English words for “weather” are outliers among European languages, while far more commonly the term that is used is the same as the word for “time”: French le temps, Romanian timpul (or the variant Slavic-rooted vremea); even the Finno-Ugric pocket of Hungary calls both time and weather by the same word: idő. Already from this lexical tour we may infer that at some earlier stage what we today call “weather” was conceptualized primarily in a phenomenological sense, as the most basic experience of “in-the-world-ness”. Yet the overlapping history of these two concepts, time and weather, should only make us wonder at the profoundly different connotations each would come to have in late modernity.
What is weather? Its etymology is not, as one may have hoped, connected to “whether”, as in “that which may be either one way, or the other” —“Whether the picnic is on or not depends on whether it rains”—, though both words have equally fascinating Germanic pedigrees. The modern German Wetter originally described the sort of ferocious wind you might encounter at a mountain peak, and later took on the primary connotation of “bad weather”, or, as is said in German, Unwetter, where the prefix that ordinarily signifies negation or absence, Un-, comes instead to indicate intensification (as in Untier — seemingly “non-animal” but literally “monster”, or Unkraut — seemingly “non-herb” but literally “weed”). At the outset then we may say that weather, strangely, is something the negative instances of which are also its paradigm instances. Yet the German and English words for “weather” are outliers among European languages, while far more commonly the term that is used is the same as the word for “time”: French le temps, Romanian timpul (or the variant Slavic-rooted vremea); even the Finno-Ugric pocket of Hungary calls both time and weather by the same word: idő. Already from this lexical tour we may infer that at some earlier stage what we today call “weather” was conceptualized primarily in a phenomenological sense, as the most basic experience of “in-the-world-ness”. Yet the overlapping history of these two concepts, time and weather, should only make us wonder at the profoundly different connotations each would come to have in late modernity. It is more than 150 years since scientists proved that
It is more than 150 years since scientists proved that  Whenever there’s a leak of documents from the remote islands and obscure jurisdictions where rich people hide their money, such as this week’s release of the
Whenever there’s a leak of documents from the remote islands and obscure jurisdictions where rich people hide their money, such as this week’s release of the